The Biology of Emotions - How They Influence Behavior
Emotions are an integral part of our human experience, acting as the driving force behind our actions and decisions. They shape our perceptions, influence our interactions, and even dictate our responses to various situations. Understanding the biology of emotions unveils the complex interplay between our brain, body, and emotional responses. It's like peeling back the layers of an onion; each layer reveals more about how we feel and why we act the way we do. This exploration not only enhances our understanding of ourselves but also equips us with the tools to navigate the intricate web of human behavior.
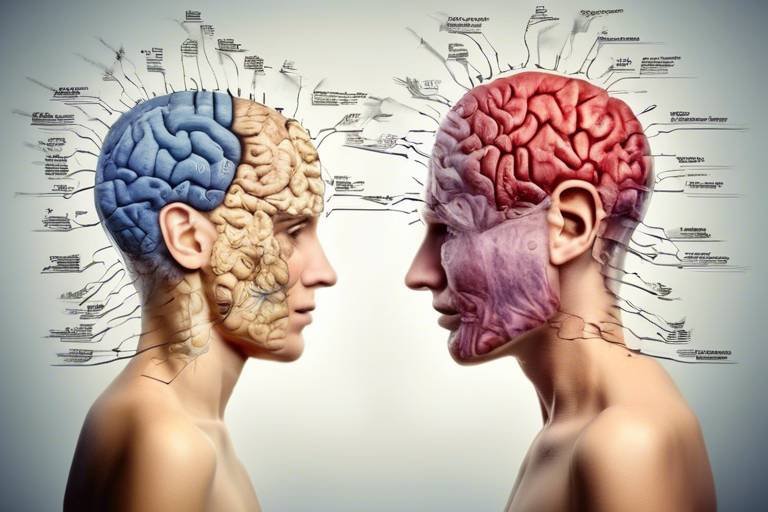
At the core of emotional responses lies the brain, a complex organ that processes feelings and regulates behavior. When we experience emotions, our brain activates specific regions that are responsible for interpreting and responding to these feelings. Imagine the brain as an orchestra, where different instruments (or regions) come together to create a symphony of emotional responses. Each section plays a unique role, contributing to the overall harmony of our emotional landscape.
As we delve deeper into the biological mechanisms of emotions, we uncover the role of neurotransmitters—those tiny chemical messengers that facilitate communication within our brains. Think of neurotransmitters as the fuel that powers our emotional engine. Chemicals like serotonin and dopamine not only influence our mood but also motivate us to pursue goals and engage with others. A deficiency in these neurotransmitters can lead to feelings of sadness or apathy, while an abundance can spark joy and enthusiasm.
Among the key players in our emotional processing is the amygdala, a small almond-shaped structure that acts as the brain's alarm system. It’s responsible for detecting threats and triggering fear responses, which can lead to quick, instinctual reactions. This is particularly important in situations where our safety is at stake. Picture the amygdala as a smoke detector; it alerts us to danger, prompting us to take action before we even have time to think.
Another vital component of emotional processing is the hippocampus, which is crucial for forming emotional memories. These memories do not merely fade away; they linger and influence our future behaviors and decisions. For instance, if you had a negative experience with a dog in your childhood, the emotional memory linked to that event may cause you to feel anxious around dogs later in life. In essence, the hippocampus helps us learn from our experiences, shaping how we react to similar situations in the future.
Regulating these emotions is the responsibility of the prefrontal cortex. This part of the brain allows us to exert self-control, manage our emotional responses, and make thoughtful decisions rather than impulsive ones. Think of the prefrontal cortex as the wise elder in a community, guiding the younger members to act with caution and consideration. When we face emotional turmoil, it's this area that helps us process our feelings and respond appropriately.
However, not all emotional experiences are positive. Stress, for instance, can significantly affect our emotional health. Chronic stress can lead to alterations in emotional responses, making us more reactive and less capable of managing our feelings. It’s like a pressure cooker; if the steam isn't released, it can lead to an explosion. Understanding the impact of stress on our emotions is essential for maintaining our overall well-being.
In our interconnected world, emotional intelligence has emerged as a crucial skill for effective communication and relationships. Recognizing and understanding our own emotions, as well as those of others, can enhance our social interactions and decision-making processes. Imagine emotional intelligence as a bridge that connects us with others, fostering empathy and understanding in our relationships.
Developing emotional intelligence is not just beneficial; it’s transformative. Simple strategies such as practicing active listening, being aware of our emotional triggers, and showing empathy can significantly improve our personal and professional relationships. By cultivating these skills, we become better equipped to navigate the complexities of human interaction, leading to more meaningful connections.
Moreover, our emotional state can profoundly impact our physical health. Research has shown a strong link between emotional well-being and conditions like heart disease and immune function. It's fascinating to consider how our feelings can affect our bodies; emotions can be both a driving force for health and a potential source of illness. This connection underscores the importance of nurturing our emotional health as a pathway to overall wellness.
- What are the main types of emotions? - Emotions can generally be categorized into basic emotions (like happiness, sadness, anger, fear, surprise, and disgust) and complex emotions (like jealousy, guilt, and pride).
- How do emotions affect decision-making? - Emotions significantly influence our choices, often guiding our decisions based on past experiences and emotional memories.
- Can emotional intelligence be developed? - Yes, emotional intelligence can be cultivated through practice, self-reflection, and learning to recognize and manage emotions.
- What is the impact of stress on emotions? - Chronic stress can lead to heightened emotional reactivity and difficulty managing feelings, affecting overall mental health.

The Role of the Brain in Emotions
Understanding how the brain processes emotions is crucial to unraveling the intricate tapestry of human behavior. Our emotions are not just fleeting feelings; they are deeply rooted in our biology and significantly influence how we interact with the world around us. The brain acts as the command center, orchestrating emotional responses that guide our decisions and actions. But what exactly happens in the brain when we feel joy, sadness, anger, or fear? Let’s dive into the key brain regions involved in emotional regulation.
At the forefront of emotional processing is the limbic system, a complex set of structures that includes the amygdala, hippocampus, and other critical areas. Each of these components plays a unique role in shaping our emotional experiences. For instance, the amygdala is often referred to as the brain's "fear center," but its functions extend beyond just fear. It helps us assess threats and triggers our fight-or-flight response, influencing our behavior in crucial moments.
Another key player is the hippocampus, which is essential for forming emotional memories. Have you ever noticed how a particular song can transport you back to a moment in time? That’s the hippocampus at work, linking emotions to specific experiences. These emotional memories can profoundly affect our future decisions, often steering us away from situations that previously caused distress or pushing us toward those that brought happiness.
Then we have the prefrontal cortex, which is like the brain’s executive function. This area is responsible for higher-order thinking, such as reasoning and self-control. It helps us regulate our emotions, allowing us to respond thoughtfully rather than react impulsively. Imagine you’re in a heated argument; the prefrontal cortex helps you take a step back, consider the consequences of your words, and choose a more constructive response.
When we talk about emotions, we can't overlook the role of neurotransmitters. These chemical messengers, including serotonin and dopamine, are vital for mood regulation and motivation. A deficiency in these chemicals can lead to mood disorders, highlighting just how intertwined our biology is with our emotional health. In fact, the balance of neurotransmitters can tilt the scale between feeling elated or experiencing deep despair.
To sum it up, the brain is a remarkable organ that manages our emotional landscape. The interplay between various brain regions and neurotransmitters creates a complex network that influences our behavior and decision-making. Understanding this relationship not only sheds light on our own emotional experiences but also opens the door to better emotional health and well-being.
- What is the primary function of the amygdala? The amygdala primarily processes emotions, especially fear, and helps trigger the fight-or-flight response.
- How does the prefrontal cortex help manage emotions? The prefrontal cortex regulates emotions by allowing for self-control and rational decision-making.
- What role do neurotransmitters play in emotions? Neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine are crucial for mood regulation and can impact our emotional responses significantly.
- Can emotional memories affect future behavior? Yes, emotional memories can guide our future decisions and reactions to similar situations.

When we dive into the fascinating world of emotions, we can't overlook the pivotal role of neurotransmitters. These chemical messengers are the unsung heroes of our emotional experiences, influencing everything from our mood to our motivation. Imagine neurotransmitters as the orchestra conductors of our brain, guiding the symphony of emotions that play throughout our lives. Without them, our emotional responses would be out of tune, leading to a cacophony of confusion and chaos.
Two of the most well-known neurotransmitters that significantly impact our emotions are serotonin and dopamine. Each of these chemicals plays a unique role in regulating our feelings and behaviors:
- Serotonin: Often dubbed the "feel-good" neurotransmitter, serotonin is crucial for maintaining mood balance. Low levels of serotonin are commonly associated with feelings of sadness and depression. Think of it as the sunshine on a cloudy day—when serotonin levels are high, we feel bright and cheerful, but when they dip, the clouds roll in, leaving us feeling down.
- Dopamine: This neurotransmitter is often linked to the brain's reward system. It fuels our motivation and drives us to seek out pleasurable experiences. Picture dopamine as the fuel that powers our emotional engine; without it, we might find ourselves stuck in neutral, lacking the drive to pursue our goals and passions.
But the story doesn't end there! Other neurotransmitters, such as norepinephrine and GABA, also play significant roles in our emotional landscape. Norepinephrine, for instance, is involved in our body's stress response, heightening our alertness and arousal during challenging situations. On the other hand, GABA acts as a calming agent, helping to regulate anxiety and promote relaxation. This delicate balance between excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters is essential for maintaining emotional stability.
Interestingly, the interplay between these neurotransmitters can also explain why certain activities or substances can dramatically alter our emotional states. For example, exercise has been shown to boost serotonin and dopamine levels, leading to feelings of happiness and fulfillment. Conversely, excessive consumption of alcohol can disrupt the balance of these neurotransmitters, often resulting in heightened feelings of sadness or anxiety the following day.
Understanding the biological underpinnings of our emotions through the lens of neurotransmitters allows us to take proactive steps in managing our emotional health. By engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support neurotransmitter production, and seeking social connections, we can foster a healthier emotional state. In essence, we hold the keys to our emotional well-being, and by tuning into the needs of our brain, we can create a more harmonious emotional experience.
- What are neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that transmit signals across synapses in the brain, influencing mood, behavior, and emotional responses. - How do serotonin and dopamine affect emotions?
Serotonin helps regulate mood and feelings of well-being, while dopamine is linked to motivation and pleasure. - Can lifestyle changes impact neurotransmitter levels?
Yes! Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and social interactions can enhance neurotransmitter function and improve emotional health.

The Amygdala's Function
The amygdala, a small almond-shaped cluster of nuclei located deep within the temporal lobes of the brain, plays a crucial role in our emotional landscape. When it comes to processing emotions, particularly fear, the amygdala is like the alarm system of our brain. Imagine walking in a dark alley and suddenly hearing a rustle in the bushes; your amygdala kicks into action, triggering a cascade of responses that prepare your body to either fight or flee. This immediate reaction is vital for survival and illustrates how the amygdala shapes our behavioral responses to perceived threats.
But the amygdala doesn’t just handle fear; it’s also involved in a wide range of emotional responses including pleasure, aggression, and even social interactions. It helps us recognize emotional cues in others, such as facial expressions, and influences our ability to empathize. For instance, when we see someone smiling, our amygdala activates, helping us feel joy and connection. On the flip side, when we perceive anger or sadness, it can evoke feelings of discomfort or concern, prompting us to react accordingly.
Interestingly, the amygdala works in tandem with other brain regions to modulate our emotional experiences. For example, the hippocampus plays a significant role in forming memories related to emotional events, while the prefrontal cortex helps us regulate our emotional responses. This collaboration ensures that our reactions are not just instinctual but also informed by past experiences and rational thought.
Moreover, the amygdala is also involved in the formation of emotional memories. These memories are often vivid and can significantly influence our future behavior. For instance, if you had a frightening experience with a dog, your amygdala will store that memory, making you more cautious around dogs in the future. This is why emotional memories can sometimes feel so intense and why they have a lasting impact on our behavior.
In summary, the amygdala is not just a fear-processing center; it is a central player in our emotional world, helping us navigate complex social situations and respond to the environment around us. Its influence on our behavior is profound, reminding us that our emotions are deeply intertwined with our biological makeup.
- What happens if the amygdala is damaged? Damage to the amygdala can result in impaired emotional responses, leading to difficulties in recognizing emotions in others and regulating one's own emotional reactions.
- Can the amygdala's response be controlled? Yes, through practices like mindfulness and cognitive behavioral therapy, individuals can learn to manage their emotional responses and reduce the amygdala's reactivity.
- How does the amygdala influence anxiety disorders? The amygdala can become hyperactive in individuals with anxiety disorders, causing exaggerated fear responses and heightened sensitivity to perceived threats.

The hippocampus is often hailed as the brain's memory center, but its role extends far beyond mere recall. It is intricately involved in the formation of emotional memories, which are essential for how we navigate our world and respond to various situations. Imagine walking into a room filled with familiar faces; the warmth of those memories can evoke feelings of joy or comfort, while a similar environment might trigger feelings of anxiety if it’s associated with past trauma. This is where the hippocampus shines, intertwining our emotional experiences with our memory.
When we encounter a significant event, the hippocampus works alongside the amygdala to encode these experiences. The amygdala, known for its role in processing emotions, particularly fear, collaborates with the hippocampus to tag memories with emotional significance. This means that not only do we remember the event itself, but we also recall the emotions tied to it. For instance, think about the first time you rode a roller coaster. You might remember the thrill and fear, the rush of adrenaline, and how you felt afterward. The hippocampus ensures that these emotional memories are stored, ready to influence your future decisions.
Moreover, emotional memories can shape our behavior in profound ways. They can inform our choices, guide our reactions, and even influence our relationships. For example, if a person has a strong emotional memory linked to betrayal, they might approach future relationships with caution, fearing a repeat of past pain. This interplay between the hippocampus and emotional memory is crucial for learning from experiences and adapting our behavior accordingly.
But what happens when this system goes awry? Issues such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can arise, where the hippocampus struggles to process and integrate traumatic memories. Individuals may find themselves reliving past traumas, as their emotional memories become overwhelming and inescapable. This highlights the delicate balance the hippocampus must maintain in managing emotional memories, which can either serve as protective mechanisms or lead to distress.
In summary, the hippocampus is not just a passive recorder of events; it actively shapes our emotional landscape. It helps us learn from our past, influences how we respond to the present, and even guides our interactions with others. Understanding the role of the hippocampus in emotional memory can provide insights into our behavior, helping us navigate the complexities of human emotion.
- What is the primary function of the hippocampus?
The hippocampus is primarily responsible for forming new memories and connecting emotions to those memories. - How do emotional memories affect behavior?
Emotional memories can influence our decisions, reactions, and relationships based on past experiences. - Can emotional memories be altered?
Yes, emotional memories can change over time due to new experiences or therapeutic interventions.

The prefrontal cortex (PFC) is often dubbed the "control center" of our brain, and for good reason. It’s the region that allows us to make sense of our emotions and regulate our reactions to them. Imagine trying to navigate a busy street without any traffic signals; that’s what life would be like without the PFC guiding our emotional responses. This area of the brain is responsible for higher-order functions such as decision-making, problem-solving, and, crucially, emotional regulation. It helps us to pause, think, and make choices that are not just instinctive but also socially acceptable.
When we experience strong emotions, such as anger or sadness, the PFC works to assess the situation and determine the most appropriate response. For instance, when faced with a stressful situation at work, the PFC can help us choose to remain calm and collected rather than lash out. This ability to regulate our emotions is essential for maintaining healthy relationships and making sound decisions. In fact, studies have shown that individuals with a well-functioning prefrontal cortex tend to have better emotional control and are less likely to engage in impulsive behaviors.
However, the PFC isn't just a passive observer; it actively interacts with other brain regions, especially the amygdala, which is responsible for processing fear and emotional responses. When we perceive a threat, the amygdala may trigger a fight-or-flight response, but it's the PFC that helps us evaluate the threat rationally. This interplay is vital for emotional balance. If the amygdala is overly reactive, it can lead to heightened anxiety or stress, while a well-functioning PFC can mitigate these feelings by providing a more measured response.
Moreover, the PFC plays a significant role in self-control. Think of it as the brakes on a speeding car; without it, we might find ourselves careening out of control emotionally. Research indicates that individuals with strong self-control, often linked to PFC activity, can better manage their emotions and avoid negative outcomes. This self-regulation is crucial not just for personal well-being but also for social interactions. When we can control our emotional responses, we are more likely to engage in constructive conversations and resolve conflicts amicably.
In addition to its role in everyday emotional regulation, the PFC is also involved in the development of emotional intelligence. Emotional intelligence refers to our ability to understand and manage our own emotions, as well as the emotions of others. A well-developed PFC allows us to empathize with others, recognize emotional cues, and respond appropriately. This skill is essential in both personal and professional contexts, enhancing our ability to connect with others and navigate social complexities.
In conclusion, the prefrontal cortex is a powerhouse of emotional regulation. It enables us to think before we act, control our impulses, and foster emotional intelligence. By understanding the vital role of the PFC, we can appreciate how our brain helps us navigate the intricate landscape of human emotions, ultimately leading to healthier interactions and decision-making processes.
- What happens if the prefrontal cortex is damaged? Damage to the PFC can lead to difficulties in emotional regulation, impulsivity, and challenges in decision-making.
- Can emotional regulation be improved? Yes, through practices such as mindfulness, cognitive behavioral therapy, and emotional intelligence training.
- How does stress affect the prefrontal cortex? Chronic stress can impair the functioning of the PFC, leading to reduced emotional control and increased impulsivity.

Stress is like a double-edged sword—it can motivate us to achieve our goals, but it can also wreak havoc on our emotional health. When we encounter stressful situations, our body enters a state of heightened alertness. This is often referred to as the "fight or flight" response, where hormones like adrenaline and cortisol flood our system, preparing us to react quickly. While this response is essential for survival, chronic stress can lead to a cascade of emotional challenges that affect our behavior and overall mental well-being.
Imagine your emotions as a delicate balance scale. When stress tips the scale, it can lead to feelings of anxiety, irritability, and even depression. For instance, have you ever felt overwhelmed by a looming deadline? That pressure can trigger a wave of negative emotions, making it difficult to concentrate or engage with others. Stress not only affects how we feel but also how we interact with the world around us.
Research shows that prolonged exposure to stress can alter brain function, particularly in areas responsible for emotional regulation. The amygdala, which processes fear and emotional responses, becomes hyperactive, leading to exaggerated reactions to everyday situations. This can create a vicious cycle: stress leads to emotional dysregulation, which in turn increases stress levels. It’s a bit like being stuck in a hamster wheel—no matter how hard you try, you just can’t seem to get off.
Furthermore, the impact of stress on emotions is not just psychological; it can manifest physically as well. Chronic stress can lead to fatigue, headaches, and even gastrointestinal issues. These physical symptoms can further exacerbate emotional distress, creating a feedback loop that is hard to break. Here’s a quick overview of how stress can influence emotional health:
| Stress Impact | Emotional Effects |
|---|---|
| Chronic Stress | Anxiety, Irritability, Depression |
| Physical Symptoms | Fatigue, Headaches, Gastrointestinal Issues |
| Behavioral Changes | Withdrawal, Increased Aggression, Impaired Decision-Making |
Managing stress is crucial for maintaining emotional health. Techniques such as mindfulness, exercise, and deep breathing can help mitigate the effects of stress. By incorporating these practices into our daily routine, we can create a buffer against the emotional turbulence that stress often brings. It’s like putting on a protective shield that allows us to navigate life’s challenges with greater ease.
In conclusion, understanding the impact of stress on our emotions is vital for fostering resilience and emotional well-being. By recognizing the signs of stress and taking proactive steps to manage it, we can improve not only our emotional health but also our relationships and overall quality of life. Remember, it’s okay to seek help when needed, whether through professional support or simply talking to a friend. After all, we’re all in this together, navigating the ups and downs of life!
- What are the common signs of stress? Common signs include irritability, anxiety, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating.
- How can I manage stress effectively? Techniques such as mindfulness, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy social support system can be beneficial.
- Can stress lead to physical health problems? Yes, chronic stress can contribute to various health issues, including heart disease, digestive problems, and weakened immune function.

Emotional intelligence (EI) is like the secret sauce that makes social interactions smoother and more enjoyable. Imagine walking into a room full of people, and you can instantly feel the vibe—who's happy, who's anxious, and who needs a friendly ear. That’s emotional intelligence at work! It’s not just about understanding your own feelings; it’s about recognizing and responding to the emotions of others, which can significantly enhance your relationships. The ability to navigate social complexities with empathy and awareness can lead to better communication, deeper connections, and a more fulfilling social life.
But why is emotional intelligence so vital in our interactions? Well, think of it this way: when you’re in tune with your own emotions, you can express yourself more clearly. You’re less likely to misinterpret others’ intentions and can respond appropriately to their feelings. This leads to stronger bonds, whether in personal relationships or professional settings. For instance, in a workplace environment, a manager with high emotional intelligence can motivate their team effectively by recognizing when someone is overwhelmed or disengaged.
Here’s an interesting fact: research shows that people with high emotional intelligence tend to have better mental health, job performance, and leadership skills. They can manage their emotions and the emotions of others, which creates a positive feedback loop of understanding and support. This not only fosters a harmonious atmosphere but also encourages collaboration and innovation. Let’s break down how emotional intelligence enhances social interactions:
- Improved Communication: High EI individuals can articulate their thoughts and feelings more effectively, reducing misunderstandings.
- Empathy: The ability to put yourself in someone else's shoes helps in forming genuine connections.
- Conflict Resolution: Those with high emotional intelligence can navigate disagreements calmly and constructively.
- Stronger Relationships: Understanding and managing emotions leads to deeper, more meaningful connections.
Moreover, emotional intelligence isn’t just a trait you either have or don’t have; it’s a skill that can be developed over time. By practicing self-awareness, managing your emotions, and improving your social skills, you can enhance your emotional intelligence. For example, try to reflect on your emotional responses in various situations and consider how they affect your interactions. This self-reflection can lead to greater awareness of your feelings and those of others.
In addition, engaging in active listening can significantly boost your emotional intelligence. When you genuinely listen to someone, you’re not just hearing their words; you’re also picking up on their emotional cues. This can help you respond in a way that acknowledges their feelings, fostering a supportive environment. The more you practice these skills, the more naturally they will come to you, transforming the way you interact with others.
In conclusion, emotional intelligence is a powerful tool that can enhance your social interactions. By becoming more aware of your own emotions and those of others, you can create deeper connections, improve communication, and navigate social situations with ease. So, whether you’re at a social gathering or a team meeting, remember that emotional intelligence can be your guiding light, making every interaction a little more meaningful.
- What is emotional intelligence? Emotional intelligence refers to the ability to recognize, understand, and manage our own emotions as well as the emotions of others.
- How can I improve my emotional intelligence? You can improve your emotional intelligence by practicing self-awareness, active listening, and empathy in your daily interactions.
- Why is emotional intelligence important? High emotional intelligence enhances communication, fosters stronger relationships, and improves conflict resolution skills.
- Can emotional intelligence be learned? Yes, emotional intelligence can be developed through practice and self-reflection.

Have you ever noticed how some people seem to navigate social situations effortlessly, while others struggle to connect? The secret often lies in their level of emotional intelligence (EI). Cultivating emotional intelligence is not just a personal development buzzword; it’s a vital skill that can enhance both your personal and professional relationships. So, how do we go about developing this crucial ability? Let’s dive into some practical strategies that can help you boost your EI.
First off, self-awareness is the cornerstone of emotional intelligence. This means being in tune with your own emotions and recognizing how they affect your thoughts and behaviors. Start by taking a few moments each day to reflect on your feelings. Ask yourself questions like, “What triggered my emotions today?” or “How did I react to that situation?” Keeping a journal can be incredibly beneficial. Write down your experiences and emotions, and over time, you’ll start to notice patterns that can help you understand your emotional responses better.
Next, let’s talk about empathy. This is the ability to understand and share the feelings of others, and it plays a crucial role in building strong relationships. To cultivate empathy, practice active listening. When someone is speaking, focus entirely on them. Put away your phone, make eye contact, and truly engage with what they are saying. You might even try to paraphrase their feelings to show that you understand. For instance, saying, “It sounds like you’re feeling overwhelmed,” can validate their emotions and foster a deeper connection.
Another key aspect of emotional intelligence is managing your emotions effectively. This involves finding healthy ways to cope with stress and frustration. Techniques such as mindfulness and meditation can be incredibly helpful. By taking time to breathe deeply and center yourself, you can create a buffer against emotional outbursts. Additionally, physical activity can also be a great way to manage emotions. Whether it’s going for a run or practicing yoga, exercise releases endorphins that can elevate your mood.
Moreover, don’t underestimate the power of feedback. Seeking constructive criticism from trusted friends or colleagues can provide valuable insights into how your emotions affect your interactions. Ask them specific questions about your behavior. For example, “Do I seem approachable during conversations?” This can help you identify areas for improvement and foster a growth mindset towards your emotional development.
Lastly, remember that cultivating emotional intelligence is a journey, not a destination. It requires consistent effort and practice. Celebrate your progress, no matter how small, and be patient with yourself. Just like building physical strength, developing emotional intelligence takes time and dedication. By embracing this process, you’ll not only enhance your own emotional well-being but also positively impact those around you.
- What is emotional intelligence? Emotional intelligence is the ability to recognize, understand, and manage our own emotions while also being able to recognize, understand, and influence the emotions of others.
- Why is emotional intelligence important? High emotional intelligence helps improve communication, reduces anxiety and stress, and enhances relationships both personally and professionally.
- Can emotional intelligence be improved? Yes, with practice and dedication, emotional intelligence can be developed through various techniques such as self-awareness exercises, empathy training, and stress management strategies.

Have you ever noticed how a bad day can leave you feeling physically drained? It’s not just in your head! The connection between emotions and physical health is profound and complex. Our emotional state can significantly influence our physical well-being, leading to a myriad of health issues if not managed properly. When we experience strong emotions, our bodies respond in ways that can either bolster our health or undermine it.
For instance, persistent stress can lead to a cascade of negative health outcomes. When we’re stressed, our bodies release hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. While these hormones are essential for short-term survival—think of them as your body’s built-in alarm system—chronic exposure can wreak havoc on your health. Studies have shown that long-term stress can contribute to conditions such as:
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Weakened immune function
The emotional toll of stress doesn’t stop there. It can also lead to unhealthy coping mechanisms, such as overeating, smoking, or drinking alcohol. These behaviors can further exacerbate physical health problems, creating a vicious cycle that is hard to break. Imagine your body as a finely tuned machine; when one part is out of sync due to emotional turmoil, the whole system can falter.
Moreover, emotions like depression and anxiety have been shown to have direct physiological effects. For example, individuals suffering from depression may experience chronic pain, fatigue, and a weakened immune system. Similarly, anxiety can lead to gastrointestinal issues, headaches, and a host of other physical ailments. It’s almost as if our emotions are communicating with our bodies, sending signals that can lead to both healing and harm.
The good news is that cultivating positive emotions can have a protective effect on our health. Engaging in activities that promote happiness and well-being—like exercising, spending time with loved ones, or practicing mindfulness—can lead to better health outcomes. For instance, research has demonstrated that individuals with a strong sense of emotional well-being tend to have lower rates of chronic diseases and better immune function. It’s like adding a layer of armor to your health!
To illustrate this connection further, consider the following table that summarizes the impact of different emotions on physical health:
| Emotion | Positive Effects | Negative Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Happiness | Boosts immune function, reduces stress | None |
| Stress | Can motivate action | Heart disease, high blood pressure |
| Depression | None | Chronic pain, fatigue |
| Anxiety | Can enhance alertness | Gastrointestinal issues, headaches |
In conclusion, the link between emotions and physical health is undeniable. By becoming more aware of our emotional states and their implications, we can take proactive steps to improve our overall health. Whether it’s through therapy, mindfulness practices, or simply taking time for self-care, nurturing our emotional health is just as important as maintaining our physical health. So, the next time you feel overwhelmed, remember that your emotions are not just feelings—they are powerful forces that can shape your health in profound ways.
- How do emotions affect physical health?
Emotions can influence various physiological processes, leading to either positive or negative health outcomes depending on the emotional state. - Can positive emotions improve my health?
Yes! Positive emotions are linked to better immune function and lower rates of chronic diseases. - What are some strategies to manage stress?
Practicing mindfulness, engaging in physical activity, and spending time with loved ones are effective ways to manage stress. - Is it possible to change my emotional responses?
Absolutely! With practice and techniques like cognitive behavioral therapy, you can learn to manage and change your emotional responses.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the role of the brain in processing emotions?
The brain plays a crucial role in how we experience and express emotions. Key regions such as the amygdala, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex work together to regulate our emotional responses. The amygdala is particularly important for processing fear and threats, while the prefrontal cortex helps us manage and control our emotions.
- How do neurotransmitters affect our emotions?
Neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine are essential for mood regulation. Serotonin is often linked to feelings of happiness and well-being, while dopamine is associated with motivation and reward. An imbalance in these chemicals can lead to mood disorders, affecting our behavior and interactions with others.
- What is the significance of emotional memory?
Emotional memories, formed in the hippocampus, play a significant role in how we react to similar situations in the future. These memories can influence our decisions and behaviors, often without us even realizing it. For instance, a past traumatic experience can shape our reactions to new challenges.
- How does stress impact our emotions?
Chronic stress can significantly alter our emotional responses, leading to heightened anxiety, irritability, and even depression. When we're stressed, our body releases hormones like cortisol, which can disrupt our emotional balance and affect our decision-making abilities.
- What is emotional intelligence and why is it important?
Emotional intelligence refers to the ability to understand and manage our emotions, as well as the emotions of others. It's essential for effective communication and building strong relationships. Higher emotional intelligence can lead to better conflict resolution and improved teamwork in both personal and professional settings.
- Can emotional well-being affect physical health?
Absolutely! There is a strong connection between our emotions and physical health. Negative emotions like stress and anxiety can contribute to health issues such as heart disease and weakened immune function. Conversely, positive emotions can enhance our overall well-being and promote better health outcomes.
- How can I cultivate emotional intelligence?
Improving emotional intelligence involves self-awareness, empathy, and effective communication. Strategies include practicing mindfulness, reflecting on your emotional responses, and actively listening to others. By enhancing these skills, you can improve your relationships and emotional well-being.