The Latest Findings on Insect Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health
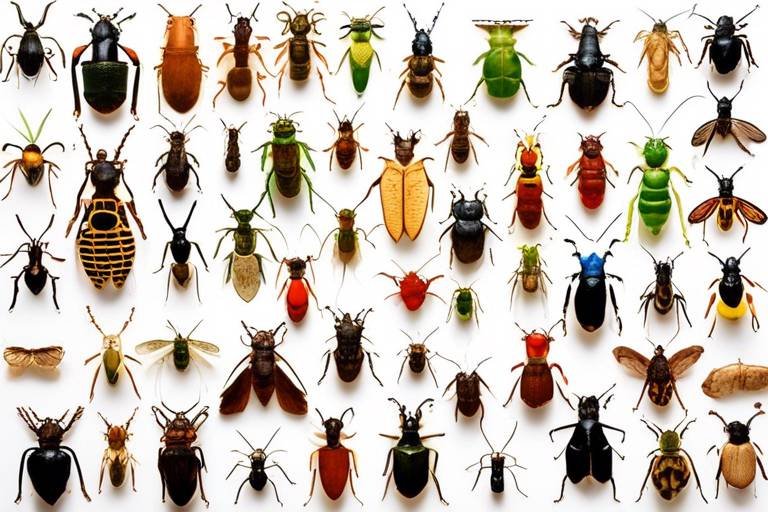
In recent years, the spotlight has been shining brightly on the fascinating world of insects and their crucial role in maintaining the health of our ecosystems. Did you know that insects make up about 80% of all known animal species? This staggering number highlights their importance in the grand tapestry of life. As we delve into the latest findings on insect biodiversity, it becomes clear that these tiny creatures are not just nuisances; they are essential players in the ecological game. From pollination to nutrient cycling, insects contribute to processes that are vital for both the environment and human survival.
Recent studies have unveiled alarming trends regarding insect populations, indicating a significant decline in diversity and abundance across various regions. This decline poses a serious threat to ecosystem functionality. For instance, when we lose certain insect species, we risk losing the services they provide, such as pollination, which is critical for the growth of many crops. Imagine a world without bees or butterflies—crops would fail, and food security would be at stake. The interconnectedness of species means that the health of one group can directly impact others, creating a domino effect that can lead to ecological collapse.
Moreover, the implications of insect biodiversity extend beyond the natural world. They intertwine with human health, agriculture, and even the economy. For example, insects play a significant role in pest control by keeping populations of harmful species in check. If insect populations dwindle, we may see an increase in pest outbreaks, leading to a greater reliance on chemical pesticides, which can create a vicious cycle of environmental degradation. Thus, understanding the dynamics of insect biodiversity is not just an ecological concern; it's a matter of global importance.
As we explore these findings, it’s essential to recognize the multifaceted threats facing insect populations today. Climate change, habitat loss, and pesticide use are just a few of the challenges that these vital organisms encounter. Research indicates that these factors not only threaten insect survival but also compromise the intricate web of life that depends on them. By addressing these challenges head-on, we can foster a healthier ecosystem and, in turn, safeguard our own future.
Insects are the unsung heroes of our ecosystems, performing tasks that many of us take for granted. They are responsible for pollinating plants, which is crucial for food production. In fact, it’s estimated that one-third of the food we consume relies on insect pollinators. Without them, our diets would be severely limited, and agricultural economies would suffer immensely. Additionally, insects contribute to nutrient cycling by breaking down organic matter, enriching soils, and promoting plant growth. This natural recycling process is essential for maintaining healthy ecosystems, highlighting the critical need to protect insect diversity.
Despite their importance, insects face a myriad of threats that jeopardize their existence. Habitat loss due to urbanization and agricultural expansion is a significant factor. As natural habitats shrink, insects lose their homes and resources, leading to population declines. Furthermore, climate change alters their habitats and life cycles, causing shifts in distribution and behavior. These changes can disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems, making it imperative to understand and mitigate these threats. One of the most pressing issues is the widespread use of pesticides, which has been linked to declining insect health and biodiversity.
Climate change is not just a distant threat; it’s a present reality that affects insect habitats and behaviors. As temperatures rise and weather patterns shift, many insect species struggle to adapt. For instance, some may migrate to cooler regions, while others may face extinction if they cannot find suitable habitats. This shift can have cascading effects on ecosystem services, as the loss of certain insect species can lead to a decline in pollination and nutrient cycling, ultimately affecting the entire food web.
Habitat fragmentation is another critical issue that disrupts insect populations. When large habitats are divided into smaller patches, insects become isolated, leading to reduced genetic diversity. This isolation increases vulnerability and extinction risks for many species. It’s like trying to survive on a tiny island when your resources are spread thin—eventually, you run out of options.
The use of pesticides has become a controversial topic in agricultural practices. While they are designed to protect crops, their impact on non-target insect populations is alarming. Studies have shown that pesticides can lead to population declines and disrupt ecological functions. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing sustainable agricultural practices that protect both crops and the insects that support them.
To combat the decline in insect biodiversity, effective conservation strategies must be implemented. This includes habitat restoration, sustainable land use practices, and public awareness campaigns to promote insect-friendly practices. By creating environments that support diverse insect populations, we can help maintain the ecological balance necessary for a healthy planet.
Insects are not just solitary players; they are integral to the functioning of ecosystems. Their decline can lead to imbalances that affect plants, animals, and even human health. The loss of pollinators, for example, threatens food security and agricultural stability. As we recognize the interconnectedness of species, it becomes clear that protecting insect biodiversity is essential for the health of our planet.
Many crops rely on insect pollinators for successful reproduction. The decline of these species threatens food security and agricultural stability, emphasizing the need for conservation efforts. Without pollinators, the variety and availability of fruits, vegetables, and nuts would drastically decrease, impacting diets and economies worldwide.
Insects provide numerous ecosystem services, from pest control to soil health. Recognizing their value is essential for promoting sustainable practices that benefit both nature and human communities. By protecting insect biodiversity, we not only ensure the health of our ecosystems but also enhance our own well-being.
- Why are insects important for ecosystems? Insects play crucial roles in pollination, nutrient cycling, and maintaining food webs, which are essential for ecosystem health.
- What are the main threats to insect populations? Major threats include habitat loss, climate change, and pesticide use, all of which contribute to declining insect diversity.
- How can we help protect insect biodiversity? Implementing conservation strategies such as habitat restoration, sustainable land use, and raising public awareness can significantly help protect insect populations.
- What is the impact of climate change on insects? Climate change alters habitats and life cycles, leading to shifts in distribution and behavior, which can disrupt ecosystem services.

The Importance of Insect Biodiversity
Insects are often overlooked in discussions about biodiversity, yet they are the unsung heroes of our ecosystems. With over a million identified species and potentially millions more yet to be discovered, insects represent the most diverse group of organisms on the planet. Their importance cannot be overstated; they contribute to critical ecological functions that sustain life on Earth. For instance, insects are key players in pollination, which is essential for the reproduction of over 75% of flowering plants, including many crops that humans rely on for food. Without insects, our plates would look very different.
Moreover, insects are instrumental in nutrient cycling. They break down organic matter, returning vital nutrients to the soil, which in turn supports plant growth. This process not only enriches the soil but also helps maintain the overall health of ecosystems. Additionally, insects serve as a crucial link in the food web, providing sustenance for a variety of animals, including birds, mammals, and even other insects. The loss of insect species could lead to a domino effect, disrupting entire ecosystems and threatening the survival of numerous other species.
To illustrate their significance, consider the following roles that insects play:
- Pollinators: Many agricultural crops depend on insects for pollination, making them vital for food security.
- Decomposers: Insects like beetles and ants break down dead organic material, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
- Pest Control: Insects such as ladybugs and lacewings naturally control pest populations, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
In summary, the biodiversity of insects is not just about the number of species; it’s about the intricate roles they play in maintaining the balance of our ecosystems. Protecting insect diversity is crucial for sustaining the health of our planet and ensuring that future generations can enjoy the benefits that come from a rich and diverse natural world.

Insects are facing a multitude of threats that are severely impacting their populations and, consequently, the health of our ecosystems. These threats are not just isolated incidents; they are interconnected and often stem from human activities that disrupt natural habitats and ecological balances. One of the most pressing issues is habitat loss, which occurs when natural environments are altered or destroyed for urban development, agriculture, and other human needs. As forests are cleared, wetlands are drained, and grasslands are converted into farmlands, the habitats that insects rely on for survival are rapidly diminishing.
Another significant threat is climate change, which is reshaping the world as we know it. Rising temperatures and shifting weather patterns are affecting the distribution and life cycles of various insect species. For instance, some insects may find their traditional habitats becoming inhospitable, forcing them to migrate to new areas. This not only affects the insects themselves but also disrupts the intricate relationships they have with plants and other animals. The result? A potential domino effect that could lead to widespread ecological disruption.
Moreover, the extensive use of pesticides in agriculture poses a grave risk to insect populations. While these chemicals are designed to eliminate pests, they often do not discriminate between harmful and beneficial insects. The decline in pollinator populations, such as bees and butterflies, is a direct consequence of pesticide exposure. This decline threatens not only the insects themselves but also the plants that depend on them for reproduction, leading to further declines in biodiversity.
To illustrate the impact of these threats, consider the following table that summarizes the primary threats to insect populations and their effects:
| Threat | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Habitat Loss | Destruction of natural environments for human development. | Reduces available habitats, leading to population declines. |
| Climate Change | Shifts in temperature and weather patterns. | Alters distribution and life cycles, causing ecosystem imbalances. |
| Pesticide Use | Widespread application of chemicals in agriculture. | Harms beneficial insects, disrupting pollination and food webs. |
In conclusion, the threats to insect populations are severe and multifaceted. Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from individuals, communities, and policymakers alike. By understanding the importance of insects and the dangers they face, we can work towards creating a more sustainable environment that not only protects these vital creatures but also secures the health of our ecosystems for generations to come.
- What is the main cause of insect population decline? The main causes include habitat loss, climate change, and pesticide use.
- Why are insects important to ecosystems? Insects play crucial roles in pollination, nutrient cycling, and serving as food for other species, maintaining ecological balance.
- How can we help protect insect populations? We can help by supporting sustainable agricultural practices, restoring habitats, and raising awareness about the importance of insects.

Climate change is not just a buzzword; it’s a reality that is reshaping our planet in profound ways. One of the most alarming impacts is on insect populations, which are experiencing significant shifts in their habitats and life cycles. Imagine a world where the buzzing of bees and the fluttering of butterflies become rare sounds. This isn't just a poetic notion; it's a potential future if we don't address the factors contributing to climate change.
As temperatures rise, insects are forced to adapt to new conditions. Some species may thrive, but many others struggle to keep up. This can lead to a phenomenon known as range shift, where insects move to higher altitudes or latitudes in search of suitable climates. For instance, studies have shown that certain butterfly species are migrating northward at alarming rates. This shift can disrupt local ecosystems, as these insects often play crucial roles in pollination and pest control.
Moreover, changes in climate can alter the timing of life cycle events, known as phenology. For example, warmer springs may cause insects to emerge earlier than usual. If plants bloom before their pollinators are active, the result can be disastrous for both. This mismatch can lead to reduced plant reproduction, which in turn affects the entire food web, including birds and mammals that rely on these plants for sustenance.
To illustrate the impact of climate change on insect populations, consider the following table that showcases various species and their responses to changing temperatures:
| Insect Species | Current Range | Projected Range Shift | Impact on Ecosystem |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monarch Butterfly | North America | Further North | Reduced pollination of native plants |
| Honeybee | Global | Variable, depending on local climate | Threatened agricultural productivity |
| Ladybug | North America | Higher Elevations | Increased aphid populations |
As you can see from the table, the implications of climate change on insect biodiversity are not just limited to the insects themselves. They ripple through the ecosystem, affecting everything from plant health to agricultural yields. It's a domino effect that can lead to significant challenges for food security and ecosystem stability.
In conclusion, the role of climate change in altering insect populations is a complex and critical issue. As stewards of the environment, we must recognize these changes and take action to mitigate their effects. Preserving insect biodiversity is not merely an environmental concern; it is essential for maintaining the balance of our ecosystems and ensuring a sustainable future for all living beings.
- How does climate change specifically affect insects? Climate change alters habitats, disrupts life cycles, and forces species to migrate, impacting their survival and ecological roles.
- What can be done to protect insect populations? Implementing conservation strategies, reducing pesticide use, and promoting sustainable agricultural practices can help protect insect biodiversity.
- Why are insects important for ecosystems? Insects play vital roles in pollination, nutrient cycling, and serving as food for other species, making them crucial for ecological balance.

Habitat fragmentation is a pressing issue that disrupts the intricate web of life that insects depend on. Imagine a once-thriving forest, bustling with the sounds of chirping insects and rustling leaves, suddenly sliced into isolated patches by roads, buildings, and agricultural fields. This scenario is not just a figment of our imagination; it’s a reality that many ecosystems face today. When habitats are fragmented, insects find themselves cut off from their natural environments, which can lead to a series of challenges that threaten their survival.
One of the most significant consequences of habitat fragmentation is the isolation of insect populations. When these populations become separated, they can no longer interbreed as freely, which diminishes genetic diversity. This lack of genetic variation makes them more vulnerable to diseases and environmental changes. Think of it like a family tree; if branches are cut off, the tree cannot grow as robustly. Insects, like any other living organism, need genetic diversity to adapt and thrive in changing conditions.
Moreover, fragmentation can lead to the loss of essential resources. Insects rely on specific plants for food, shelter, and breeding. When their habitats are fragmented, these resources may become scarce or completely unavailable. For example, pollinators like bees need access to a variety of flowering plants to sustain their populations. If their habitat is divided, they may not find enough food sources, leading to population declines. This situation creates a ripple effect, as their decline can negatively impact the plants that depend on them for pollination.
Additionally, fragmented habitats can expose insects to new threats. For instance, when habitats are broken up, they may come into closer contact with urban areas and agricultural lands where pesticides are heavily used. This increased exposure can lead to higher mortality rates among insect populations, further exacerbating their decline. The interconnectedness of species means that when one group suffers, it can lead to a domino effect, impacting other organisms within the ecosystem.
To illustrate the impact of habitat fragmentation on insect populations, consider the following table that summarizes key effects:
| Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Isolation | Separation of populations leading to decreased genetic diversity. |
| Resource Scarcity | Loss of food and shelter due to fragmented habitats. |
| Increased Vulnerability | Higher exposure to pesticides and environmental changes. |
Addressing habitat fragmentation requires a concerted effort from individuals, communities, and policymakers. Strategies such as creating wildlife corridors, restoring native habitats, and promoting sustainable land-use practices can help mitigate the effects of fragmentation. By reconnecting fragmented landscapes, we can support insect populations and, in turn, the health of our ecosystems. After all, insects are not just small creatures; they are the unsung heroes of our environment, playing crucial roles that often go unnoticed.
- What is habitat fragmentation? Habitat fragmentation refers to the process by which larger habitats are divided into smaller, isolated patches, often due to human activities.
- Why is insect biodiversity important? Insect biodiversity is vital for ecosystem health as insects contribute to pollination, nutrient cycling, and food webs.
- How can we help combat habitat fragmentation? We can help by supporting conservation efforts, restoring natural habitats, and advocating for sustainable land-use practices.

Pesticides are often hailed as a miracle solution for protecting crops from pests and diseases, but their impacts on insect populations can be devastating. While they serve a purpose in agriculture, the collateral damage they inflict on non-target species, particularly beneficial insects, raises serious concerns about their long-term sustainability. The widespread use of these chemicals has resulted in alarming declines in insect biodiversity, which in turn disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems.
One of the most concerning effects of pesticide use is the phenomenon known as bioaccumulation. This occurs when pesticides accumulate in the bodies of insects over time, leading to higher concentrations of toxins in their systems. As these insects are consumed by predators, the toxins can magnify up the food chain, ultimately affecting birds, mammals, and even humans. This interconnectedness highlights the importance of considering the broader ecological ramifications of pesticide application.
Moreover, pesticides can interfere with the reproductive systems of insects, leading to reduced fertility rates and altered behaviors. For example, studies have shown that exposure to certain pesticides can impair the navigation abilities of pollinators like bees, making it difficult for them to find food and return to their hives. This not only threatens the survival of these crucial pollinators but also poses a risk to food security, as many crops depend on their pollination.
In addition to direct toxicity, pesticides can also disrupt the natural pest control mechanisms that insects provide. Predatory insects, such as ladybugs and lacewings, help keep pest populations in check. When pesticides kill these beneficial insects, it can lead to an increase in pest populations, creating a cycle of dependency on chemical controls that further harms the environment.
To illustrate the severity of pesticide impacts, consider the following table that summarizes key effects on insect populations:
| Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Bioaccumulation | Accumulation of pesticides in insect bodies, leading to higher concentrations in the food chain. |
| Reproductive Impairment | Reduced fertility and altered behaviors in insect populations, particularly pollinators. |
| Disruption of Natural Pest Control | Decline of predatory insects leading to increased pest populations and reliance on chemical controls. |
As we become more aware of these impacts, it is essential to advocate for sustainable agricultural practices that minimize pesticide use. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies, which emphasize the use of biological controls and habitat management, can reduce reliance on harmful chemicals while promoting healthy insect populations. Educating farmers and consumers about the importance of insect biodiversity is crucial for fostering a more sustainable approach to agriculture.
- What are the main types of pesticides? Pesticides can be categorized into several types, including insecticides, herbicides, fungicides, and rodenticides, each targeting specific pests.
- How do pesticides affect pollinators? Pesticides can impair the navigation, foraging, and reproductive abilities of pollinators, leading to population declines.
- What are some alternatives to chemical pesticides? Alternatives include biological pest control, crop rotation, and the use of resistant crop varieties.
- Why is insect biodiversity important? Insect biodiversity supports ecosystem services such as pollination, nutrient cycling, and pest control, which are vital for healthy ecosystems.

To combat the alarming decline in insect biodiversity, we must implement effective conservation strategies that not only protect these vital creatures but also enhance the ecosystems they inhabit. One of the most impactful approaches is habitat restoration. This involves rehabilitating degraded environments to create suitable conditions for insects to thrive. For instance, replanting native flora can provide food and shelter for various insect species, which in turn supports the entire food web.
Another crucial strategy is promoting sustainable land use. This means adopting agricultural practices that minimize harm to insect populations while still meeting human needs. Techniques like crop rotation, organic farming, and integrated pest management can significantly reduce the reliance on harmful pesticides while enhancing soil health and biodiversity. By encouraging farmers to implement these methods, we not only protect insect life but also ensure the long-term viability of our food systems.
Public awareness campaigns play a vital role in conservation efforts. Educating communities about the importance of insects and how they contribute to ecosystem health can inspire individuals to adopt insect-friendly practices in their daily lives. Simple actions, such as creating pollinator gardens, reducing pesticide use in home gardens, and supporting local wildlife, can collectively have a substantial impact. It’s about fostering a culture that values and protects our insect allies.
Furthermore, collaboration among government bodies, NGOs, and local communities is essential. This can take the form of conservation programs that focus on specific regions or threatened species. For instance, initiatives that protect wetlands or grasslands can create safe havens for various insect populations. By pooling resources and expertise, we can develop comprehensive strategies that address the multifaceted challenges facing insects today.
Lastly, research and monitoring are critical components of any conservation strategy. By understanding the specific needs and behaviors of different insect species, we can tailor our conservation efforts more effectively. This might involve tracking population trends, studying the effects of climate change on their habitats, or assessing the impact of various agricultural practices. The more we know, the better equipped we are to safeguard these essential organisms.
- Why are insects important for ecosystems?
Insects play crucial roles in pollination, nutrient cycling, and serving as food for other animals, making them essential for ecological balance. - What are the main threats to insect populations?
Major threats include habitat loss, climate change, and pesticide use, all of which jeopardize their survival and the health of ecosystems. - How can I help protect insect biodiversity?
You can create insect-friendly gardens, reduce pesticide use, and support local conservation efforts to help protect these vital species.

Insects are not just tiny creatures buzzing around; they are the unsung heroes of our ecosystems. Their presence is woven into the very fabric of nature, creating a complex web of interactions that sustain life on Earth. Think of insects as the glue that holds the ecosystem together. Without them, many other species would struggle to survive. For example, pollinators like bees and butterflies are essential for the reproduction of many flowering plants. If these insects were to disappear, we would witness a dramatic decline in plant diversity, which in turn would affect the animals that rely on those plants for food and shelter.
The decline of insect populations can trigger a chain reaction that disrupts the balance of entire ecosystems. When insect numbers dwindle, it can lead to overpopulation of certain species, particularly herbivores, which can devastate plant life. This imbalance can further result in the loss of habitat for other animals, creating a ripple effect throughout the food web. For instance, fewer insects mean less food for birds, amphibians, and small mammals, ultimately leading to a decline in their populations as well.
Moreover, insects contribute to nutrient cycling by breaking down organic matter, which enriches the soil and promotes plant growth. This process is crucial for maintaining healthy ecosystems. When insects are removed from this equation, the soil quality deteriorates, affecting agricultural productivity and the overall health of the environment. Without healthy soils, we face challenges in food production, which directly impacts human health and well-being.
To illustrate the interconnectedness of species, consider the following table that highlights some key relationships:
| Insect Species | Role in Ecosystem | Dependent Species |
|---|---|---|
| Bees | Pollination | Fruits, Vegetables, Birds |
| Ants | Soil Aeration | Plants, Other Insects |
| Butterflies | Pollination | Flowers, Birds |
| Beetles | Decomposition | Plants, Soil Microbes |
This table illustrates just a few of the many ways insects interact with their environment and other species. Each insect plays a unique role, and their decline can have unforeseen consequences. It's crucial to recognize that the health of our ecosystems is intricately linked to the health of insect populations.
In conclusion, the interconnectedness of species emphasizes the need for conservation efforts. Protecting insects means safeguarding the delicate balance of our ecosystems, ensuring that all species, including humans, can thrive. As we move forward, let’s remember that every insect counts and that their well-being is a reflection of our planet’s health.
- Why are insects important for ecosystems? Insects play critical roles in pollination, nutrient cycling, and serving as food for other animals, making them essential for ecosystem health.
- What are the main threats to insect populations? Major threats include habitat loss, climate change, and pesticide use, all of which can lead to population declines.
- How can I help protect insect biodiversity? You can help by creating insect-friendly gardens, reducing pesticide use, and supporting conservation initiatives.

When we think about the food on our plates, we often overlook the tiny heroes that make it all possible: insect pollinators. These remarkable creatures, including bees, butterflies, and even some beetles, play a crucial role in the reproduction of many crops. In fact, it is estimated that around 75% of the world’s flowering plants rely on animal pollinators, and this includes a significant portion of the fruits, vegetables, and nuts that we consume daily. Imagine biting into a juicy apple or enjoying a sweet strawberry; these delights are possible largely because of the diligent work of insects.
However, the decline of pollinator populations poses a serious threat to food security. As insect populations dwindle due to factors like habitat loss, climate change, and pesticide use, the availability of these essential crops is jeopardized. This not only affects the diversity of our diets but also has economic implications, particularly for farmers who depend on healthy yields. A study published in the journal Nature highlighted that the economic value of pollination services provided by insects is estimated to be worth over $200 billion globally each year. That’s a staggering number, and it underscores just how interconnected our food systems are with insect health.
To illustrate the impact of pollinator decline, consider the following table that shows the relationship between pollinator populations and crop yields:
| Crop Type | Dependence on Insect Pollination | Potential Yield Loss (%) if Pollinators Decline |
|---|---|---|
| Fruits (e.g., apples, cherries) | High | 30-50% |
| Nuts (e.g., almonds) | Very High | 90% |
| Vegetables (e.g., cucumbers, squash) | Moderate | 20-30% |
| Grains (e.g., wheat, rice) | Low | 5-10% |
This table clearly demonstrates that crops with high dependence on insect pollination could face significant yield losses if we continue to ignore the plight of pollinators. It's not just about the taste of our food; it’s about the very foundation of our food systems. Without these insects, we risk a future where our plates are less colorful and our diets less nutritious.
So, what can we do to support these vital pollinators? Simple actions can make a big difference. Planting native flowers, reducing pesticide use, and supporting local farmers who practice sustainable agriculture are just a few ways we can contribute. By fostering environments that are friendly to insects, we not only help them thrive but also ensure that our food systems remain robust and resilient.
- Why are insects important for pollination? Insects transfer pollen from one flower to another, which is essential for plant reproduction and fruit production.
- What are the main threats to pollinator populations? Habitat loss, climate change, pesticide use, and diseases are the primary threats facing pollinators today.
- How can I help protect pollinators? You can plant pollinator-friendly plants, avoid using pesticides, and support local organic farms.

Insects are not just tiny creatures buzzing around; they are the unsung heroes of our ecosystems, providing a plethora of ecosystem services that significantly enhance human well-being. Imagine a world without bees, butterflies, and beetles—sounds bleak, right? These little champions contribute to the environment in ways that are often overlooked. They play a critical role in processes such as pollination, nutrient cycling, and pest control, which are essential for maintaining the balance of our ecosystems.
Take pollination, for example. Approximately 75% of the world's flowering plants depend on insects for their reproduction. This includes many of the fruits, vegetables, and nuts that we consume daily. Without these industrious pollinators, our food supply would dwindle, leading to increased prices and food scarcity. The loss of insect pollinators can lead to a domino effect, threatening not just our diets but also the livelihoods of farmers and the agricultural industry as a whole.
Furthermore, insects contribute to nutrient cycling by breaking down organic matter and returning vital nutrients to the soil. This process is crucial for the health of our ecosystems, as it ensures that plants receive the nutrients they need to grow. Insects like earthworms and dung beetles play a pivotal role in this cycle, enhancing soil fertility and structure. Healthy soil translates to healthy crops, which ultimately supports human nutrition and economic stability.
Insects also act as natural pest controllers. Predatory insects, such as ladybugs and lacewings, help keep pest populations in check, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. This not only protects the environment but also promotes safer food production practices. By fostering a diverse insect population, we can create a more resilient agricultural system that benefits both nature and humanity.
To illustrate the importance of insects in ecosystem services, consider the following table that highlights various services provided by insects and their direct impact on human well-being:
| Ecosystem Service | Description | Impact on Human Well-being |
|---|---|---|
| Pollination | Insects facilitate the reproduction of flowering plants. | Supports food production and biodiversity. |
| Nutrient Cycling | Decomposers break down organic matter, enriching soil. | Enhances agricultural productivity and soil health. |
| Pest Control | Predatory insects regulate pest populations. | Reduces reliance on harmful pesticides and promotes sustainable farming. |
Ultimately, the decline of insect populations poses a serious threat to these ecosystem services, which can have far-reaching consequences for human health and well-being. As we face challenges such as climate change and habitat loss, it is crucial to recognize the value of insects and implement practices that support their survival. By fostering a healthy insect population, we not only protect our ecosystems but also ensure a sustainable future for ourselves and generations to come.
- Why are insects important for the environment? Insects play key roles in pollination, nutrient cycling, and pest control, which are vital for maintaining ecosystem balance.
- How does the decline of insect populations affect food security? Many crops rely on insect pollinators. Their decline can lead to reduced crop yields, threatening food availability and prices.
- What can be done to protect insect biodiversity? Implementing sustainable agricultural practices, restoring habitats, and raising public awareness are crucial steps to protect insect populations.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Why is insect biodiversity important for ecosystems?
Insect biodiversity is crucial because insects perform essential functions such as pollination, nutrient cycling, and serving as food for other species. Without a diverse insect population, the balance of ecosystems can be disrupted, leading to negative effects on plant growth, animal populations, and even human food sources.
- What are the main threats to insect populations?
Insect populations face several significant threats, including habitat loss due to urbanization and agriculture, climate change affecting their habitats and life cycles, and the widespread use of pesticides that can harm their health and reduce their populations. Each of these factors can have devastating impacts on their survival and the ecosystems they support.
- How does climate change affect insects?
Climate change alters temperature and weather patterns, which can shift insect habitats and affect their life cycles. For instance, warmer temperatures may lead to earlier breeding seasons, while extreme weather events can destroy habitats. These changes can disrupt the timing of pollination and other ecological interactions, ultimately impacting the entire food web.
- What is habitat fragmentation, and why is it a problem for insects?
Habitat fragmentation occurs when large habitats are broken into smaller, isolated patches, often due to human activities like deforestation and urban development. This isolation can reduce genetic diversity among insect populations, making them more vulnerable to extinction and less resilient to environmental changes.
- How do pesticides impact insect health?
Pesticides are designed to kill pests, but they can also harm beneficial insects, including pollinators. Exposure to these chemicals can lead to population declines, disrupt reproductive processes, and impair immune functions. Understanding these impacts is vital for developing sustainable agricultural practices that protect insect health.
- What conservation strategies can help protect insect biodiversity?
Effective conservation strategies include habitat restoration to create supportive environments for insects, promoting sustainable land-use practices, and raising public awareness about the importance of insects. Engaging communities in insect-friendly practices, such as planting native species and reducing pesticide use, can also make a significant difference.
- How are insects connected to human food security?
Many crops depend on insect pollinators for successful reproduction. The decline of these pollinators can lead to reduced crop yields and threaten food security. By protecting insect populations, we can ensure the stability of agricultural systems and the availability of diverse food sources for humans.
- What ecosystem services do insects provide?
Insects contribute to numerous ecosystem services, including pest control, soil aeration, and nutrient cycling. They help maintain healthy ecosystems, which in turn support human well-being. Recognizing and valuing these services is crucial for promoting sustainable practices that benefit both nature and people.