The Intersection of Technology and Historical Research
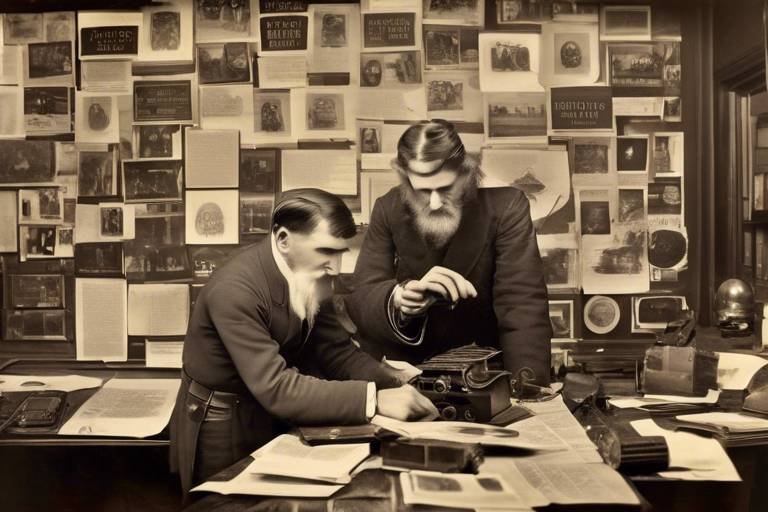
In today's fast-paced world, the marriage of technology and historical research is nothing short of revolutionary. Imagine being able to sift through centuries of documents from the comfort of your home. This is the reality we live in, where modern technology enhances the way we understand our past. From digital archives to advanced data analysis tools, the tools available to historians are transforming their methodologies and expanding the horizons of what we can learn about history.
Gone are the days when historians had to rely solely on dusty old books and limited access to physical archives. Now, researchers can explore vast collections of historical documents at the click of a button. This unprecedented access not only makes research more efficient but also allows for a diversity of perspectives that were previously hard to come by. The impact of these digital resources is profound, enabling scholars to uncover hidden narratives and challenge traditional interpretations. In essence, technology is not just a tool; it is a gateway to a richer understanding of our shared human experience.
Moreover, the integration of data analysis tools into historical research has allowed historians to process large datasets in ways that were unimaginable just a few decades ago. What if you could uncover patterns and trends that reveal the ebb and flow of societal changes over time? With these advanced tools, historians can do just that. They can analyze everything from census data to newspaper articles, unveiling insights that can reshape our understanding of historical events.
For instance, consider the power of text mining. This technique allows researchers to delve into historical texts at scale, extracting valuable insights that can lead to new interpretations. By analyzing the language used in documents from a particular era, historians can gauge the sentiments and attitudes of people during that time. This brings us to the fascinating realm of sentiment analysis, which can be applied to historical documents to understand public opinion and emotional responses. Imagine reading a letter from a soldier during a war and being able to quantify the fear or hope expressed within it. This kind of analysis provides a deeper understanding of societal attitudes and the emotional landscape of different periods.
Furthermore, network analysis opens up new avenues for exploration. By visualizing relationships between historical figures, events, and ideas, historians can reveal the intricate social and political dynamics that shaped our world. It’s like piecing together a complex puzzle where every connection matters. This analytical approach helps to paint a clearer picture of how events are interrelated and how they influence one another.
Additionally, the advent of geospatial technologies, such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS), allows historians to map historical events and trends geographically. This capability offers fresh perspectives on how location influences historical developments. For instance, mapping the routes of migration can provide insights into cultural exchanges and the spread of ideas, making history not just a series of events but a tapestry of human experience woven through space and time.
As we delve deeper into the intersection of technology and historical research, we also encounter the exciting realm of virtual reality (VR). Imagine stepping into a VR simulation that transports you to a historical site or event. This immersive experience can significantly enhance engagement and understanding of historical contexts through experiential learning. It’s like time travel, where you can walk through ancient cities or witness pivotal moments in history as if you were really there.
Interactive exhibits utilizing VR technology can bring history to life in ways that traditional methods simply cannot match. Visitors can experience historical events and environments in a more impactful and memorable way. This not only captivates the audience but also fosters a deeper connection to the past, making history feel relevant and alive.
In educational settings, the applications of VR in historical research are proving to be invaluable. Students can explore and understand historical narratives through innovative tools that engage their senses and stimulate their curiosity. This approach transforms learning from a passive experience into an active exploration, encouraging students to ask questions and seek answers in ways that traditional textbooks may not inspire.
As we continue to explore this fascinating intersection of technology and historical research, it becomes clear that we are only scratching the surface of what is possible. The future of history is bright, and with each technological advancement, we are offered new lenses through which to view our past.
- How has technology changed historical research? Technology has revolutionized access to documents, allowing researchers to analyze vast datasets and uncover new insights.
- What is text mining? Text mining is a technique used to analyze large volumes of text to extract meaningful information and insights.
- What role does virtual reality play in history? VR offers immersive experiences that enhance understanding and engagement with historical contexts.
- Can sentiment analysis be applied to historical documents? Yes, sentiment analysis can gauge public opinion and emotional responses in historical texts, providing deeper insights into societal attitudes.
- What is network analysis in historical research? Network analysis visualizes relationships between historical figures and events, revealing social and political dynamics.

Digital Archives
This article explores how modern technology enhances historical research, examining tools, methodologies, and the impact of digital resources on understanding the past.
In the age of information, have emerged as a game-changer for historians and researchers alike. Imagine being able to explore a treasure trove of historical documents without ever leaving your home. With just a few clicks, you can access vast collections that were once locked away in dusty libraries or archives, waiting for the right scholar to unlock their secrets. This transformation has not only increased accessibility but has also significantly broadened the scope and depth of historical research.
Digital archives have democratized access to information, allowing anyone with an internet connection to delve into the past. Whether you are a seasoned historian or a curious student, these archives provide a wealth of resources that can enhance your understanding of historical events and figures. For instance, you can find everything from manuscripts and photographs to government records and newspaper articles all in one place. This accessibility has led to a surge in public interest in history, as more people can engage with their heritage and the stories that have shaped our world.
Moreover, digital archives often come equipped with powerful search tools that make finding specific information a breeze. You can search by keywords, dates, or even specific events, allowing you to pinpoint the exact documents you need for your research. This capability transforms the traditional research process, which could take months or even years, into a much more efficient endeavor. For instance, a historian studying the American Civil War can quickly locate letters, diaries, and official records that provide firsthand accounts of the era, all thanks to these advanced search functionalities.
Additionally, many digital archives offer interactive features that enhance the research experience. Users can annotate documents, share findings with peers, and even collaborate on projects in real-time. This fosters a sense of community among researchers and encourages the sharing of knowledge and insights. The ability to connect with others who share similar interests is a powerful motivator and can lead to groundbreaking discoveries.
However, it's important to acknowledge that while digital archives are incredibly valuable, they also come with their own set of challenges. Issues such as digital preservation and accessibility must be addressed to ensure that these resources remain available for future generations. As technology evolves, so too must our strategies for preserving the past. Institutions must invest in robust systems to safeguard digital content from obsolescence and ensure that all users can access these resources, regardless of their technological capabilities.
In conclusion, digital archives represent a revolutionary advancement in historical research, providing unprecedented access to information and fostering collaboration among scholars. As we continue to explore the intersection of technology and history, it’s clear that these digital resources will play a pivotal role in shaping our understanding of the past. So, the next time you find yourself curious about a historical event, remember that a world of knowledge is just a click away, waiting to be discovered.
- What are digital archives? Digital archives are online collections of historical documents, photographs, and other resources that can be accessed via the internet.
- How do digital archives benefit researchers? They provide easy access to a wide range of historical materials, enhance research efficiency, and foster collaboration among scholars.
- Are there any challenges associated with digital archives? Yes, challenges include digital preservation and ensuring accessibility for all users.

Data Analysis Tools
In the realm of historical research, the advent of has been nothing short of revolutionary. These tools empower historians to sift through mountains of data, revealing patterns and insights that were previously invisible. Imagine diving into a vast ocean of historical records, where each wave represents a different dataset. Without the right tools, it can feel like trying to find a needle in a haystack. But with advanced data analysis techniques, historians can not only locate that needle but also understand its significance in the broader narrative of history.
One of the most exciting aspects of modern data analysis is how it allows researchers to handle large datasets effectively. For instance, consider the impact of social media on contemporary history. By analyzing tweets, posts, and comments, historians can gain insights into public sentiment during key events. This ability to process and analyze data at scale transforms the way we interpret history. Instead of relying solely on traditional sources, historians can now incorporate digital footprints into their research, offering a more comprehensive view of the past.
Among the various methodologies available, text mining stands out as a powerful technique. This approach enables researchers to examine historical texts on a grand scale, extracting valuable information and uncovering new interpretations. For example, by applying text mining to letters, diaries, or newspapers from a specific period, historians can identify recurring themes, sentiments, and even shifts in public opinion. This not only enriches our understanding of historical narratives but also opens doors to new questions and avenues of inquiry.
Another fascinating application of data analysis tools is sentiment analysis. This technique allows historians to gauge public opinion and emotional responses from historical documents. Imagine being able to quantify the feelings expressed in letters written during a war or a political upheaval. By analyzing the language used, researchers can uncover the emotional landscape of society at that time. This deeper understanding of societal attitudes provides context to historical events, making them more relatable and comprehensible.
Furthermore, network analysis is an invaluable tool for historians. It helps visualize relationships between historical figures, events, and ideas, revealing intricate social and political dynamics that shaped history. For instance, by mapping out connections between key players in a historical event, researchers can identify how alliances formed, how information flowed, and how decisions were made. This method not only enhances our understanding of individual actions but also highlights the interconnectedness of historical narratives.
In summary, the integration of data analysis tools into historical research has opened up a world of possibilities. By harnessing the power of technology, historians can uncover hidden patterns, gain deeper insights, and ultimately tell more compelling stories about our past. As we continue to embrace these advancements, the study of history will not only evolve but also become increasingly relevant in our understanding of contemporary issues.
- What are data analysis tools? Data analysis tools are software applications that help researchers process and analyze large datasets to extract meaningful insights.
- How does text mining work? Text mining involves using algorithms to analyze text data, identifying patterns, themes, and sentiments within historical documents.
- What is sentiment analysis? Sentiment analysis is a technique used to evaluate the emotional tone behind a series of words, helping to understand public opinion in historical contexts.
- Why is network analysis important in history? Network analysis helps historians visualize relationships and interactions between historical figures and events, revealing the complexities of social and political dynamics.

Text Mining
Text mining is a fascinating and powerful technique that allows historians to delve deep into the vast sea of historical texts. Imagine having the ability to sift through thousands of documents in a matter of seconds, extracting meaningful patterns and insights that could take a lifetime to uncover manually. This is the magic of text mining! By employing advanced algorithms and computational methods, researchers can analyze large volumes of text to identify trends, themes, and relationships that might otherwise remain hidden.
At its core, text mining transforms the way we interpret historical narratives. Rather than relying solely on traditional methods of close reading, historians can now leverage technology to conduct quantitative analyses of texts. This approach opens up a world of possibilities, allowing for the exploration of questions that were previously too daunting to tackle. For instance, historians can analyze the frequency of certain words or phrases over time, revealing shifts in public sentiment or cultural focus.
One of the most exciting aspects of text mining is its ability to facilitate new interpretations of historical contexts. Let's consider a few key applications:
- Keyword Analysis: By identifying frequently used terms, historians can gauge what topics were most relevant during a specific time period.
- Co-occurrence Analysis: This technique examines how often certain words appear together, shedding light on relationships between different historical figures or events.
- Topic Modeling: This method helps in discovering abstract topics within a collection of texts, allowing researchers to categorize and summarize large datasets effectively.
Furthermore, text mining can be particularly useful in uncovering voices that have been marginalized throughout history. By analyzing letters, diaries, and other personal documents, researchers can bring to light the experiences of individuals who may not have been included in mainstream historical narratives. This democratization of history is crucial for a more inclusive understanding of our past.
As we embrace the digital age, the integration of text mining into historical research not only enhances our understanding of the past but also invites a new generation of scholars to explore history through a modern lens. It’s a thrilling time to be involved in historical research, where the intersection of technology and humanities leads to groundbreaking discoveries and deeper insights.

Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis is a fascinating tool that allows historians to dive deeper into the emotional undercurrents of historical documents. Imagine being able to read between the lines of letters, speeches, or newspaper articles from the past and gauge the feelings and opinions of people who lived through those times. This technique employs natural language processing (NLP) algorithms to analyze text, identifying whether the sentiment expressed is positive, negative, or neutral. By doing so, historians can uncover a wealth of information about public sentiment during specific events or periods, leading to a richer understanding of history.
For instance, consider how sentiment analysis can be applied to political speeches. By analyzing the language used by leaders during pivotal moments, researchers can assess how public sentiment shifted in response to their rhetoric. This not only provides insights into the leaders' strategies but also reveals how the populace reacted emotionally to significant events, such as wars, elections, or social movements.
Furthermore, sentiment analysis can be particularly illuminating when applied to social media data. In today's digital age, platforms like Twitter and Facebook serve as modern-day public forums, where individuals express their thoughts and feelings about current events. By examining historical tweets or posts related to specific events, historians can track sentiment trends over time, offering a contemporary parallel to historical sentiment analysis.
To illustrate the impact of sentiment analysis on historical research, consider the following table that summarizes some key findings from recent studies:
| Event | Sentiment Shift | Key Insights |
|---|---|---|
| World War I | Negative to Neutral | Initial enthusiasm shifted to disillusionment and despair. |
| Civil Rights Movement | Positive Growth | Increased optimism as public support grew over time. |
| COVID-19 Pandemic | Negative Spike | Heightened fear and anxiety reflected in social media discourse. |
As the table demonstrates, sentiment analysis can reveal profound shifts in public emotions tied to significant historical events. This analytical approach not only enhances our understanding of the past but also invites us to consider how emotions have shaped societal trajectories. By applying sentiment analysis, historians can piece together a more nuanced narrative, acknowledging that history is not just a series of events but a tapestry woven with human emotions.
In conclusion, sentiment analysis serves as a bridge between the past and present, allowing us to explore the emotional landscapes of historical contexts. It empowers historians to ask new questions and uncover layers of meaning that traditional methods might overlook. As technology continues to advance, the potential for sentiment analysis to transform our understanding of history is boundless, opening up exciting avenues for future research.
- What is sentiment analysis? Sentiment analysis is a technique used to identify and categorize the emotional tone behind a series of words, often used in analyzing historical texts to understand public sentiment.
- How does sentiment analysis benefit historical research? It allows historians to uncover emotional responses and societal attitudes during specific periods, providing a richer context for understanding historical events.
- Can sentiment analysis be applied to modern social media? Yes, it can analyze social media data to track public sentiment trends over time, offering insights into contemporary societal attitudes.

Network Analysis
Network analysis is like putting on a pair of special glasses that allow historians to see the intricate web of relationships that have shaped our past. Imagine trying to understand a complex novel without knowing how the characters are connected; that's what studying history without network analysis can feel like. By using this powerful tool, researchers can map out connections between historical figures, events, and ideas, revealing the underlying social and political dynamics that have influenced historical outcomes.
At its core, network analysis involves the examination of nodes and edges—where nodes represent entities such as people, organizations, or events, and edges represent the relationships or interactions between them. This method can uncover surprising links and associations that traditional historical methods might overlook. For instance, a historian studying a political movement might discover how seemingly unrelated activists were actually part of a larger, interconnected network that influenced the movement’s success.
One fascinating application of network analysis is in the study of correspondence between historical figures. By analyzing letters exchanged between influential individuals, researchers can visualize the flow of ideas and alliances. This not only sheds light on personal relationships but also reveals how these connections impacted broader historical events. For example, the correspondence between key figures during the American Revolution can illustrate how ideas spread and evolved within a network of revolutionary thinkers.
Moreover, network analysis can also extend to the examination of cultural phenomena. Consider the impact of social networks in the spread of art movements or scientific ideas. By mapping these relationships, historians can gain insights into how certain trends gained momentum and how they were influenced by the interplay of various social groups. This approach can lead to a richer understanding of the cultural landscape during specific periods.
To illustrate the power of network analysis, let’s take a look at a simplified example:
| Node | Type | Connections |
|---|---|---|
| Thomas Jefferson | Historical Figure | John Adams, Benjamin Franklin, James Madison |
| Declaration of Independence | Document | Thomas Jefferson, John Adams, Benjamin Franklin |
| American Revolution | Event | Thomas Jefferson, George Washington, John Adams |
This table shows just a few nodes and their connections, but imagine the complexity when you scale it up to include hundreds or even thousands of entities! The insights gained from such analyses can significantly alter our understanding of historical narratives.
Ultimately, network analysis acts as a powerful lens through which we can examine the past. It encourages historians to think beyond linear narratives and consider the multifaceted relationships that have shaped our world. By embracing these modern methodologies, we can uncover the hidden stories that lie within the fabric of history, making it not just a series of events, but a rich tapestry of interconnected lives and ideas.
- What is network analysis in historical research? Network analysis is a method used to examine the relationships between historical figures, events, and ideas by visualizing them as nodes and edges.
- How can network analysis change our understanding of history? It reveals hidden connections and influences that traditional methods might miss, providing a deeper insight into the dynamics of historical events.
- What tools are used for network analysis? Various software tools, such as Gephi and NodeXL, are used to create visualizations and analyze complex networks in historical research.

Geospatial Technologies
Geospatial technologies are at the forefront of transforming historical research, providing historians with innovative tools to visualize and analyze historical data in ways that were previously unimaginable. These technologies, including Geographic Information Systems (GIS), satellite imagery, and spatial analysis tools, empower researchers to map out historical events, trends, and movements across different geographical locations. Imagine being able to see the migration patterns of ancient civilizations or the spread of ideas during significant historical periods—all through interactive maps and data visualizations!
One of the most exciting aspects of geospatial technologies is their ability to uncover hidden connections between historical events and physical locations. By layering historical data over modern maps, historians can pinpoint where significant events took place and how geography influenced these occurrences. For instance, a historian studying the American Civil War can use GIS to analyze battle locations, troop movements, and even the impact of terrain on military strategies. This not only provides a clearer picture of the events but also allows for a deeper understanding of the context in which they occurred.
Furthermore, geospatial technologies facilitate the analysis of spatial relationships and patterns. For example, researchers can examine how urban development has changed over centuries by comparing historical maps with current geographic data. This can reveal how cities evolved, which areas were significant during particular periods, and how social dynamics shifted in response to geographical changes. Such insights can lead to new interpretations of historical narratives, challenging long-held beliefs and offering fresh perspectives.
To illustrate the impact of geospatial technologies on historical research, let's consider a few applications:
- Mapping Historical Events: Researchers can create detailed maps that show the locations of significant events, such as battles, treaties, or cultural exchanges, allowing for a visual representation of history.
- Analyzing Demographic Changes: By overlaying historical population data with geographic information, historians can study migration patterns and demographic shifts over time.
- Climate and Environmental Studies: Understanding how climate and geography affected historical developments can provide insights into how societies adapted to their environments.
As we move forward, the integration of geospatial technologies into historical research is likely to expand even further. With advancements in data collection methods, such as drones and remote sensing, historians will have access to even more precise and comprehensive datasets. This will not only enhance the accuracy of historical research but also enrich our understanding of the intricate relationship between geography and history.
Q: What are geospatial technologies?
A: Geospatial technologies refer to tools and methods that collect, analyze, and visualize geographic data, including GIS, remote sensing, and spatial analysis.
Q: How do geospatial technologies aid historical research?
A: These technologies allow historians to map historical events, analyze spatial relationships, and uncover patterns that enhance our understanding of the past.
Q: Can anyone access geospatial tools for historical research?
A: Yes, many geospatial tools and resources are available online, making it easier for researchers and enthusiasts to explore historical data.

Virtual Reality Experiences
In recent years, Virtual Reality (VR) has emerged as a groundbreaking tool in the realm of historical research, enabling scholars and enthusiasts alike to delve into the past in ways that were once unimaginable. Imagine stepping into the shoes of a Roman soldier, walking the streets of ancient Pompeii, or witnessing a pivotal moment in history unfold right before your eyes. This immersive technology not only captivates the imagination but also enhances our understanding of historical events and contexts.
One of the most exciting aspects of VR in historical research is its ability to create interactive experiences. Unlike traditional methods of learning, which often involve passive consumption of information, VR allows users to engage actively with historical environments. For example, users can explore a 3D reconstruction of the Great Wall of China or navigate through a digitally recreated medieval castle, making history feel tangible and alive. This level of engagement fosters a deeper emotional connection to the past, transforming the way we perceive historical narratives.
Furthermore, VR experiences can be tailored to suit various educational needs. Educators are increasingly incorporating VR into their curricula to provide students with an innovative way to explore history. Imagine a history class where students can virtually visit the Battle of Gettysburg or the signing of the Declaration of Independence. Such experiences can spark curiosity and foster a love for history that textbooks alone may not inspire.
The potential applications of VR in historical research are vast, and they are continually evolving. Here are some notable examples of how VR is being utilized:
- Reenactments: Users can participate in or observe historical reenactments, gaining insights into the motivations and experiences of individuals from the past.
- Site Preservation: VR can help preserve endangered historical sites by creating detailed digital replicas that can be accessed even if the physical sites are lost.
- Public Engagement: Museums and cultural institutions are using VR to attract visitors, offering them unique experiences that enhance their understanding of history.
As we look to the future, it’s clear that VR will continue to play a pivotal role in the way we study and interpret history. By bridging the gap between the past and the present, VR not only makes historical research more accessible but also more engaging. The ability to visualize and interact with historical events in a virtual space opens up new avenues for exploration and understanding, making history not just a subject to study, but an experience to live.
What is Virtual Reality in historical research?
Virtual Reality (VR) in historical research refers to the use of immersive technology to create interactive experiences that allow users to explore and engage with historical events, environments, and figures.
How can VR enhance learning in history?
VR enhances learning by providing immersive experiences that foster emotional connections to historical events, making them more relatable and memorable than traditional learning methods.
Are there any drawbacks to using VR for historical research?
While VR offers many benefits, it can also be expensive to implement and may require specialized knowledge to create effective content. Additionally, there may be concerns about the accuracy of virtual representations.

Interactive Exhibits
Imagine walking through a museum and suddenly finding yourself in the midst of a bustling medieval market, surrounded by merchants hawking their wares and townsfolk going about their daily lives. This is the magic of , where history isn't just something you read about in textbooks but something you can experience firsthand. With the advent of technologies like virtual reality (VR), museums and educational institutions are transforming the way we engage with the past.
Interactive exhibits allow visitors to immerse themselves in historical contexts, making learning not just informative but also exciting. These exhibits utilize advanced technologies to create environments that replicate historical events or settings. For instance, a visitor might don a VR headset and find themselves on the battlefield of a significant war, witnessing the strategies employed by leaders and the bravery of soldiers. This kind of engagement fosters a deeper understanding of history, as it connects emotional experiences with factual knowledge.
Moreover, interactive exhibits can cater to various learning styles. Some people grasp concepts better through visual stimuli, while others might benefit from hands-on experiences. By incorporating elements like augmented reality (AR), touchscreens, and interactive displays, these exhibits can appeal to a broad audience. Imagine a touchscreen that allows you to explore the family tree of a prominent historical figure or an AR app that overlays historical images onto current landscapes, providing a visual link between the past and present.
In addition to enhancing individual learning experiences, interactive exhibits also foster social interaction. Visitors can engage with each other as they navigate through the exhibit, share insights, and discuss their interpretations of historical events. This collaborative aspect enriches the learning experience, creating a community of history enthusiasts who can learn from one another.
As we look to the future, the potential for interactive exhibits is limitless. With ongoing advancements in technology, the possibilities for creating more immersive and engaging historical experiences are expanding. For instance, the integration of artificial intelligence could allow for personalized tours based on a visitor's interests, making history even more accessible and relatable.
In summary, interactive exhibits represent a significant leap forward in how we present and understand history. They break down the barriers between the past and the present, making history come alive in ways that traditional methods simply cannot. As we continue to embrace these innovations, we can expect a richer, more engaging exploration of our shared human experience.
- What are interactive exhibits? Interactive exhibits are engaging displays that allow visitors to actively participate in their learning experience, often utilizing technology like virtual reality and augmented reality.
- How do interactive exhibits enhance learning? They provide immersive experiences that connect emotional engagement with factual knowledge, catering to different learning styles and fostering social interaction among visitors.
- What technologies are used in interactive exhibits? Common technologies include virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), touchscreens, and advanced data visualization tools.
- Can interactive exhibits be found in all museums? While many modern museums are incorporating interactive elements, the availability of such exhibits varies by institution and their commitment to using technology in education.

Educational Applications
In the realm of historical research, Virtual Reality (VR) is not just a futuristic concept; it's a powerful educational tool that is reshaping how students and enthusiasts engage with the past. Imagine stepping into the shoes of a Roman citizen or walking through the bustling streets of medieval Europe. With VR, this is not only possible but also incredibly immersive. By using VR technology, educators can provide students with experiences that are far more engaging than traditional textbooks. Why read about the pyramids when you can explore them in 3D?
One of the most exciting aspects of VR in education is its ability to foster a deeper connection to historical events. Students can witness pivotal moments in history firsthand, such as the signing of the Declaration of Independence or the landing at Normandy. This kind of experiential learning can ignite a passion for history that might otherwise remain dormant. The emotional weight of seeing history unfold in a virtual space can lead to a profound understanding of the context and significance of these events.
Moreover, VR can cater to different learning styles, making history accessible to a wider range of students. For visual learners, the rich graphics and interactive environments can help solidify concepts that might seem abstract in a written format. Kinesthetic learners, on the other hand, can benefit from the hands-on experiences that VR offers, allowing them to engage with history in a way that feels tangible and real.
To illustrate the impact of VR in education, consider the following table that highlights some of the key benefits:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Immersive Learning | Students experience historical events as if they were actually there, enhancing retention and understanding. |
| Accessibility | VR makes history accessible to students with different learning styles, engaging them in unique ways. |
| Increased Engagement | Interactive experiences foster greater interest and enthusiasm for learning about history. |
| Critical Thinking | Students analyze and interpret historical events, encouraging deeper cognitive engagement. |
Additionally, educational applications of VR can extend beyond the classroom. Museums and historical sites are beginning to incorporate VR into their exhibits, allowing visitors to engage with history on a whole new level. Imagine walking through a museum where you can don a VR headset and suddenly find yourself in the middle of a historical reenactment. This not only makes learning fun but also encourages a more active form of participation in history.
In conclusion, the integration of VR into educational applications is revolutionizing how we teach and learn about history. By providing immersive, interactive experiences, VR is not just enhancing educational outcomes; it is transforming the way we connect with our past. So, the next time you think about history, consider the possibilities that VR can offer. Are you ready to step into history?
- What is Virtual Reality (VR)? - VR is a technology that creates a simulated environment, allowing users to immerse themselves in a 3D world.
- How can VR enhance historical education? - VR allows students to experience historical events and environments in an interactive way, making learning more engaging and memorable.
- Are there any risks associated with using VR in education? - While VR is generally safe, it can cause discomfort in some users, such as motion sickness. It's essential to monitor usage and provide breaks as needed.
- What are some examples of VR applications in history? - Examples include virtual tours of historical sites, reenactments of significant events, and interactive museum exhibits.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How has technology changed historical research?
Technology has significantly transformed historical research by providing access to digital archives, advanced data analysis tools, and geospatial technologies. Researchers can now explore vast collections of historical documents online, analyze large datasets for hidden patterns, and visualize historical events geographically, making the study of history more comprehensive and insightful.
- What are digital archives and why are they important?
Digital archives are online repositories that house a wide range of historical documents and artifacts. They are important because they revolutionize access to historical materials, allowing researchers and the public to explore documents from anywhere in the world, thus enhancing the scope and depth of historical research.
- What role do data analysis tools play in historical research?
Data analysis tools enable historians to process and analyze large datasets efficiently. They help uncover patterns and trends that may not be immediately obvious, transforming how history is studied and interpreted. This allows historians to develop new insights and perspectives on past events.
- Can you explain text mining in the context of historical research?
Text mining involves using computational techniques to analyze large volumes of text. In historical research, it allows scholars to extract valuable insights from historical texts at scale, facilitating new interpretations of narratives and contexts that might have been overlooked in traditional research methods.
- What is sentiment analysis, and how is it applied to historical documents?
Sentiment analysis is a technique used to determine the emotional tone behind a series of words. When applied to historical documents, it can help gauge public opinion and emotional responses during specific periods, providing a deeper understanding of societal attitudes and cultural contexts.
- How does network analysis benefit historians?
Network analysis helps historians visualize relationships among historical figures, events, and ideas. By revealing intricate social and political dynamics, it allows researchers to understand how these relationships shaped historical developments and influenced the course of events.
- What are geospatial technologies, and why are they valuable in historical research?
Geospatial technologies, such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS), allow historians to map historical events and trends geographically. They provide valuable insights into how location influences historical developments, helping researchers to analyze the spatial dimensions of history.
- How does virtual reality enhance the study of history?
Virtual reality (VR) creates immersive experiences that transport users to historical sites or events. This experiential learning enhances engagement and understanding of historical contexts, making the study of history more impactful and memorable for students and researchers alike.
- What are interactive exhibits, and how do they relate to historical research?
Interactive exhibits utilize VR technology to bring history to life. They allow visitors to experience historical events and environments in a more engaging way, fostering a deeper connection to the past and enhancing the overall educational experience.
- How are educational applications of VR shaping historical research?
Educational applications of VR provide innovative tools for students to explore and understand historical narratives. By offering immersive learning experiences, they help students develop a stronger connection to history and encourage critical thinking about past events.