The Role of Technology in Modern Archaeology
In today's fast-paced world, the intersection of technology and archaeology is nothing short of revolutionary. Gone are the days when archaeologists relied solely on trowels and brushes to uncover the past. Now, with the advent of cutting-edge tools and methodologies, we are witnessing a transformation in how we study and understand ancient cultures and their artifacts. This article delves into the myriad ways technology has reshaped archaeological practices, enhancing research methodologies, preservation techniques, and public engagement. So, how exactly has technology changed the game for archaeologists? Let's explore this fascinating evolution together!
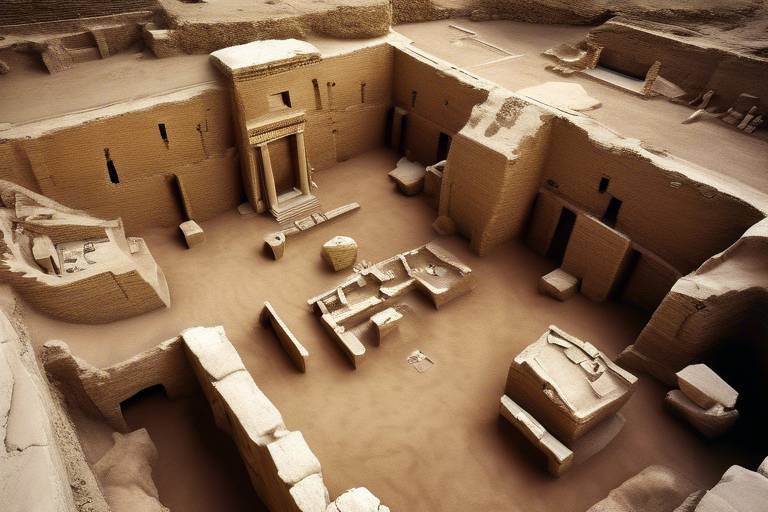
One of the most significant advancements in modern archaeology is the use of remote sensing technologies. Tools like LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) and satellite imagery empower archaeologists to survey vast areas with remarkable efficiency. Imagine being able to uncover hidden structures and landscapes without ever lifting a shovel! These technologies allow researchers to visualize the terrain and identify potential sites of interest from above, revealing secrets that lie beneath the surface. This not only saves time and resources but also minimizes the environmental impact of excavation.
Another groundbreaking development is the use of 3D modeling tools, which provide archaeologists with the ability to recreate artifacts and sites in a digital format. This technology offers immersive experiences that enhance the understanding of historical contexts for both researchers and the public. Picture this: you can explore a digitally reconstructed ancient city right from your living room! The ability to visualize these sites in three dimensions allows for deeper insights into the lives of our ancestors.
One specific technique within 3D modeling is photogrammetry. This method enables the creation of accurate 3D models from photographs, facilitating detailed analysis of artifacts and sites. By taking multiple images from different angles, archaeologists can compile a comprehensive digital record. This not only aids in analysis but also plays a crucial role in preserving these items for future study and public engagement. Imagine being able to study a fragile artifact without ever having to touch it!
Creating digital records of artifacts through photogrammetry significantly benefits conservation efforts. It allows for analysis and restoration without the physical handling of delicate items, thus preserving their integrity. The digital models can serve as reference points for future restorations, ensuring that the original details are not lost over time. This approach is akin to having a time capsule of knowledge that can be revisited and studied without risking damage to the original artifacts.
Moreover, 3D models and visualizations make archaeological findings more accessible to the public. They provide educational resources and virtual tours that engage wider audiences in archaeological discoveries. Imagine students being able to take a virtual field trip to an ancient site, exploring its history and significance without ever leaving their classrooms. This democratization of knowledge fosters a greater appreciation for cultural heritage and encourages more people to take an interest in archaeology.
The collaboration between archaeologists and computer scientists has led to innovative solutions for data analysis. By combining expertise in these fields, researchers can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of archaeological investigations. This interdisciplinary approach is like blending the analytical prowess of computer science with the rich narratives of archaeology, resulting in a more profound understanding of ancient civilizations.
Another technological marvel in archaeology is the use of Geographic Information Systems (GIS). GIS technology allows archaeologists to analyze spatial relationships and patterns in archaeological data. This capability provides invaluable insights into ancient human behavior, settlement patterns, and environmental interactions. With GIS, researchers can visualize how ancient communities adapted to their surroundings, revealing the intricate connections between people and their environments.
Using GIS, researchers can reconstruct historical landscapes, enabling them to understand how ancient civilizations interacted with their environments. This process is akin to piecing together a giant jigsaw puzzle, where each piece represents a different aspect of human history. By analyzing spatial data, archaeologists can uncover the stories of how ancient peoples thrived, migrated, and transformed their landscapes over time.
GIS tools also assist in managing archaeological sites by monitoring changes over time. This helps prioritize preservation efforts and ensures the protection of cultural heritage. By keeping track of site conditions and potential threats, archaeologists can take proactive measures to safeguard these invaluable resources. It's like having a guardian watching over our shared history, ensuring that future generations can appreciate and learn from it.
Artificial intelligence is increasingly being utilized to analyze large datasets, identify patterns, and predict archaeological sites. This revolutionary approach is transforming the way researchers approach their work, making discoveries more efficient and effective. Imagine having a digital assistant that can sift through mountains of data and highlight potential excavation sites based on historical trends!
Machine learning algorithms can process vast amounts of archaeological data, uncovering trends and making connections that may not be immediately apparent to human researchers. This technology enhances the overall understanding of ancient cultures, allowing archaeologists to draw new conclusions and formulate fresh hypotheses. It's like having a powerful magnifying glass that reveals hidden details in the tapestry of human history.
Predictive modeling techniques help archaeologists identify potential excavation sites based on historical data. This significantly improves the chances of discovering new artifacts and sites of interest. By analyzing patterns and trends from previous excavations, researchers can make informed predictions about where to dig next. It's akin to following a treasure map, where each clue leads to exciting new discoveries waiting to be uncovered.
- How has technology changed archaeology? Technology has revolutionized archaeology by introducing tools like remote sensing, GIS, and AI, which enhance research methodologies and public engagement.
- What is photogrammetry? Photogrammetry is a technique that creates accurate 3D models from photographs, aiding in the analysis and conservation of artifacts.
- Why is GIS important in archaeology? GIS helps analyze spatial relationships in archaeological data, providing insights into ancient human behavior and settlement patterns.
- How does AI assist archaeologists? AI analyzes large datasets to identify patterns and predict potential excavation sites, making archaeological discoveries more efficient.

Advancements in Remote Sensing
The world of archaeology has witnessed a remarkable transformation in recent years, primarily due to the advent of remote sensing technologies. These innovations, including LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) and satellite imagery, have revolutionized the way archaeologists conduct surveys and gather data. Imagine being able to survey vast areas of land without ever needing to dig a single hole; that’s the power of remote sensing! By utilizing these technologies, researchers can uncover hidden structures and landscapes that would otherwise remain buried beneath layers of soil and vegetation.
LiDAR, for instance, employs laser pulses to create incredibly detailed topographical maps. This method can penetrate dense forest canopies, revealing ancient ruins and pathways that are invisible to the naked eye. In many cases, LiDAR has led to the discovery of entire cities that were previously unknown, reshaping our understanding of ancient civilizations. Similarly, satellite imagery provides a broader perspective, allowing archaeologists to observe large geographical areas and identify potential sites of interest from space.
But how exactly do these technologies enhance archaeological practices? Here are a few key benefits:
- Efficiency: Remote sensing allows archaeologists to cover large areas in a fraction of the time it would take using traditional methods.
- Cost-Effectiveness: By reducing the need for extensive fieldwork, these technologies can significantly lower project costs.
- Data Richness: The data collected through remote sensing is often more comprehensive, providing insights into the spatial relationships and distribution of archaeological features.
Moreover, the integration of remote sensing with Geographic Information Systems (GIS) further amplifies its potential. By combining these technologies, archaeologists can analyze spatial data in ways that were previously unimaginable. For example, they can overlay historical maps with modern satellite images to track changes in the landscape over time, revealing how ancient cultures adapted to their environments.
As we delve deeper into the 21st century, the role of remote sensing in archaeology is only expected to grow. With ongoing advancements in technology, such as improved algorithms for data analysis and the increasing availability of high-resolution satellite images, researchers are poised to unlock even more secrets of our past. The future of archaeology is undoubtedly bright, and remote sensing is at the forefront of this exciting journey.

3D Modeling and Visualization
In the realm of archaeology, have become game-changers, transforming how we study and engage with the past. Imagine being able to walk through ancient ruins without ever stepping foot on the site! With advanced technology, this is now a reality. By leveraging sophisticated software and techniques, archaeologists can create detailed digital representations of artifacts and archaeological sites, allowing for an immersive experience that was previously unimaginable.
One of the most significant advantages of 3D modeling is its ability to recreate artifacts in a way that highlights their intricate details. For example, a delicate pottery shard can be scanned and transformed into a virtual model that showcases every curve and color, providing insights into the craftsmanship of ancient cultures. This not only aids researchers in their studies but also captivates the public's interest, making history more relatable and engaging.
Moreover, these digital models serve multiple purposes. They can be used for educational purposes, allowing students and enthusiasts to explore historical contexts from the comfort of their homes. Imagine a classroom where students can interact with a 3D model of an ancient Egyptian tomb, examining its layout and significance without the need for a physical field trip. This level of accessibility opens doors to a wider audience, fostering a deeper appreciation for our shared heritage.
One of the key techniques behind 3D modeling in archaeology is photogrammetry. This method involves taking multiple photographs of an object or site from various angles, which are then processed to create a highly accurate 3D representation. The beauty of photogrammetry lies in its ability to capture even the most intricate details, making it an invaluable tool for researchers. For instance, consider how a simple object like a coin can tell a story of trade and culture when recreated in three dimensions. The visual representation allows for a deeper analysis of its inscriptions and designs, revealing insights into the civilization that produced it.
Beyond just visualization, photogrammetry plays a crucial role in conservation efforts. By creating digital records of artifacts, archaeologists can analyze and restore items without the need for physical handling. This is particularly important for delicate items that may be damaged by touch or exposure to the elements. The digital models serve as a reference point for restoration, ensuring that the integrity of the original artifact is maintained. This practice not only preserves the artifacts themselves but also protects the cultural narratives they embody.
As we embrace the digital age, the potential for public engagement through 3D models and visualizations grows exponentially. Virtual tours and online exhibitions allow anyone with an internet connection to explore archaeological findings, breaking down geographical barriers. Whether it's a virtual walk through the ruins of Pompeii or an interactive exhibit showcasing ancient tools, these digital experiences invite curiosity and exploration. As a result, archaeology becomes a shared journey, where the past is not just for scholars but for everyone eager to learn about human history.
In summary, the integration of 3D modeling and visualization into archaeological practices is redefining how we understand and interact with ancient cultures. As technology continues to evolve, so too will our methods of exploration and education, ensuring that the stories of our ancestors remain alive and accessible for generations to come.
- What is 3D modeling in archaeology? 3D modeling involves creating digital representations of artifacts and archaeological sites, allowing for detailed analysis and public engagement.
- How does photogrammetry work? Photogrammetry captures multiple photographs of an object from different angles, which are then processed to create a 3D model.
- Why is 3D modeling important for conservation? It allows for the analysis and restoration of artifacts without physical handling, preserving their integrity and historical significance.
- How can the public access 3D archaeological models? Many institutions offer virtual tours and online exhibitions that showcase 3D models, making archaeology accessible to a wider audience.

Applications of Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry has emerged as a revolutionary tool in the field of archaeology, allowing researchers to create detailed and accurate 3D models of artifacts and archaeological sites. This technique involves taking multiple photographs from different angles and using software to stitch these images together, resulting in a digital representation that can be analyzed and studied without the need for physical handling. Imagine being able to walk around a digital replica of an ancient temple or a long-lost artifact right from your computer—this is the magic of photogrammetry!
The applications of photogrammetry in archaeology are vast and varied. For instance, it enables the documentation of fragile artifacts that might be too delicate to touch. By creating a digital record, archaeologists can study the item in detail while preserving its original form. This method is particularly beneficial for items that are at risk of deterioration due to environmental factors or human interaction. Additionally, photogrammetry facilitates the sharing of findings with the public and other researchers, as these digital models can be easily disseminated online.
One of the most exciting aspects of photogrammetry is its ability to enhance public engagement with archaeology. Museums and educational institutions are increasingly using 3D models created through photogrammetry to provide interactive experiences for visitors. Imagine walking into a museum and being able to explore a digital version of an ancient site, manipulating the model to see it from different angles or zooming in on intricate details. This not only makes archaeology more accessible but also fosters a deeper appreciation for our shared human history.
In practice, photogrammetry can be applied in various ways, including:
- Site Documentation: Capturing the layout and features of archaeological sites for future reference.
- Artifact Analysis: Creating detailed models of artifacts to study their features and context without physical handling.
- Virtual Reconstructions: Recreating historical sites and environments to understand ancient civilizations better.
The integration of photogrammetry into archaeological practices not only enhances the accuracy of data collection but also opens up new avenues for research. By preserving the integrity of artifacts and sites, archaeologists can ensure that future generations have access to invaluable cultural heritage. The ability to analyze and share findings in a digital format promotes collaboration and innovation within the field, ultimately leading to a more comprehensive understanding of our past.
As technology continues to advance, the potential for photogrammetry in archaeology seems limitless. Researchers are exploring ways to combine this technique with other technologies, such as Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR), to create even more immersive experiences. The future of archaeology is not only about digging into the ground; it's about digging into the digital realm to uncover the secrets of ancient cultures.
1. What is photogrammetry?
Photogrammetry is a technique that uses photographs taken from various angles to create accurate 3D models of objects or environments. In archaeology, it helps in documenting artifacts and sites without physical handling.
2. How does photogrammetry benefit archaeological research?
It allows for detailed analysis of artifacts, preserves the integrity of delicate items, and makes findings more accessible to the public through digital models.
3. Can photogrammetry be used for site management?
Yes, photogrammetry can document the condition of archaeological sites over time, helping in monitoring changes and prioritizing preservation efforts.
4. Is photogrammetry accessible for educational purposes?
Absolutely! Many museums and educational institutions utilize photogrammetry to create interactive experiences, allowing visitors to engage with archaeological findings in a digital format.

Benefits for Conservation
In the world of archaeology, the preservation of artifacts is paramount, and photogrammetry is proving to be a game-changer. By creating detailed digital records of artifacts, this technology allows archaeologists to analyze and restore items without the need for physical handling. Imagine being able to study a delicate ancient vase without ever touching it—this is the reality that photogrammetry offers!
Not only does this method protect fragile objects from wear and tear, but it also facilitates a more thorough examination. With high-resolution images and 3D models, researchers can zoom in on intricate details that might be missed during a traditional hands-on analysis. This leads to a deeper understanding of the artifacts' materials, craftsmanship, and historical significance.
Moreover, the digital records created through photogrammetry can serve as a permanent archive. In the event of damage or loss, these digital replicas can be used for restoration efforts, ensuring that the essence of the artifact is preserved for future generations. Think of it as a digital safety net, capturing the essence of cultural heritage in a way that is both innovative and essential.
Additionally, the accessibility of these digital models enhances educational outreach. Museums and educational institutions can utilize these resources to create engaging exhibits and virtual tours, allowing the public to interact with history in a way that was previously unimaginable. This not only fosters a greater appreciation for cultural heritage but also encourages a broader dialogue about conservation efforts.
In summary, the benefits of photogrammetry for conservation are vast and multifaceted, including:
- Protection: Minimizes physical handling of artifacts.
- Detailed Analysis: Enables thorough examination of intricate details.
- Permanent Archives: Creates digital replicas for restoration and study.
- Public Engagement: Enhances educational outreach through accessible resources.
As technology continues to evolve, the integration of these methods into archaeological practices will undoubtedly lead to more effective conservation strategies, ensuring that our understanding of the past remains intact for future exploration.
Q: What is photogrammetry?
A: Photogrammetry is a technique that uses photography to measure and create 3D models of objects and spaces, allowing for detailed analysis without physical handling.
Q: How does photogrammetry aid in conservation?
A: It creates digital records of artifacts, which can be analyzed and restored without touching the original items, thus preserving their integrity.
Q: Can the public access 3D models created through photogrammetry?
A: Yes, many museums and educational institutions are using these models to create virtual tours and interactive exhibits that engage the public.
Q: What are the long-term benefits of using technology in archaeology?
A: Technology enhances research accuracy, improves conservation methods, and makes archaeological findings more accessible to the public, fostering a greater appreciation for cultural heritage.

Public Accessibility
The advent of 3D modeling and visualization technologies has significantly transformed the way archaeological findings are shared with the public. Imagine walking through a digital replica of an ancient city, exploring its streets, and peering into homes that were built thousands of years ago. This is now possible thanks to the innovative use of technology in archaeology. By creating interactive 3D models of artifacts and sites, researchers can invite the public to engage with history in a way that was previously unimaginable. For instance, virtual reality experiences allow users to immerse themselves in historical contexts, making learning about ancient cultures not just informative but also incredibly engaging.
Moreover, these digital resources serve as valuable educational tools for schools and universities. Educators can incorporate these models into their curriculum, providing students with a hands-on learning experience that enhances their understanding of archaeology and history. The ability to view artifacts from multiple angles and in different contexts helps students grasp the significance of these items beyond their physical form. It’s like having a time machine at your fingertips, allowing you to witness history unfold in a visually stunning manner.
Additionally, the accessibility of these resources extends to a global audience. With just an internet connection, anyone can explore archaeological sites and artifacts from the comfort of their home. This democratization of knowledge not only fosters a greater appreciation for cultural heritage but also encourages a sense of responsibility towards preserving these treasures. As more people engage with archaeology through digital platforms, there is a growing recognition of the importance of protecting our shared history.
Furthermore, many archaeological projects are now making use of social media and online platforms to share their discoveries in real-time. Live-streaming excavations or posting updates on social media allows enthusiasts and the general public to follow along with archaeological work as it happens. This level of transparency and engagement helps to cultivate a passionate community of history lovers and encourages dialogue about the significance of archaeological findings.
In summary, the integration of 3D modeling and visualization tools in archaeology has not only enhanced the way researchers study artifacts and sites but has also opened up new avenues for public engagement. By making archaeological findings more accessible, we are fostering a deeper understanding and appreciation of our collective past, ensuring that the stories of ancient cultures continue to resonate with future generations.
- What is 3D modeling in archaeology?
3D modeling in archaeology involves creating digital representations of artifacts and sites, allowing for detailed analysis and public engagement. - How does technology enhance public access to archaeology?
Technology, such as virtual reality and online platforms, makes archaeological findings more accessible to a wider audience, fostering education and engagement. - Can I explore archaeological sites online?
Yes! Many archaeological projects offer virtual tours and 3D models that can be accessed online, allowing anyone to explore these sites from home.

Collaboration with Computer Science
The intersection of archaeology and computer science is a fascinating realm that has opened up new avenues for research and discovery. As technology continues to advance at breakneck speed, archaeologists are increasingly turning to computer scientists for innovative solutions to complex problems. This collaboration is not just beneficial; it’s revolutionary. Imagine archaeologists armed with powerful algorithms and data analysis tools, diving into the depths of ancient cultures with unprecedented precision. By harnessing the power of technology, they can sift through mountains of data in a fraction of the time it would take using traditional methods.
One of the most significant contributions of computer science to archaeology is the development of sophisticated data analysis techniques. For instance, with the help of machine learning, archaeologists can analyze vast datasets—such as satellite imagery and excavation records—to identify patterns and correlations that may have gone unnoticed. This means that researchers can not only better understand the past but also make predictions about where to dig next. It’s like having a treasure map that points to hidden gems of history!
Moreover, the use of big data analytics allows archaeologists to compile and analyze information from various sources, including historical texts, environmental data, and cultural artifacts. This comprehensive approach provides a richer context for understanding ancient civilizations. For example, by analyzing climate data alongside archaeological findings, researchers can gain insights into how environmental changes influenced human behavior and settlement patterns. This kind of interdisciplinary work is vital, as it fosters a holistic understanding of the past.
Additionally, the collaboration extends beyond just data analysis. Computer scientists are also developing virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) applications that bring archaeological sites to life. Imagine stepping into a VR reconstruction of an ancient city, walking its streets, and interacting with its inhabitants—this is no longer science fiction but a tangible reality thanks to the partnership between these two fields. Such immersive experiences not only enhance research but also engage the public, making archaeology more accessible and exciting.
Furthermore, the integration of computer science into archaeology is facilitating the creation of digital repositories where artifacts can be cataloged and analyzed without the need for physical handling. This is particularly crucial for fragile items that require sensitive handling. By digitizing artifacts, researchers can conduct detailed studies while preserving the integrity of these precious items for future generations. In this way, technology not only aids in research but also plays a crucial role in conservation efforts.
In summary, the collaboration between archaeology and computer science is a powerful alliance that is transforming how we explore and understand our past. By leveraging advanced technologies, archaeologists can uncover hidden narratives and provide a more nuanced view of ancient cultures. As this partnership continues to evolve, we can only anticipate even more exciting discoveries on the horizon.
- How is technology changing archaeological practices?
Technology enhances archaeological practices by providing tools for data analysis, remote sensing, and virtual reconstructions, allowing for more efficient and informed research. - What role does machine learning play in archaeology?
Machine learning helps archaeologists analyze large datasets to identify patterns and make predictions about potential excavation sites. - Can virtual reality be used in archaeology?
Yes, virtual reality is used to create immersive experiences that allow researchers and the public to explore ancient sites and artifacts digitally. - What are the benefits of digital repositories?
Digital repositories preserve fragile artifacts and allow for detailed analysis without physical handling, aiding in conservation efforts.

Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Geographic Information Systems, commonly referred to as GIS, have revolutionized the field of archaeology by providing powerful tools for analyzing spatial data. This technology enables archaeologists to visualize and interpret complex datasets, leading to deeper insights into ancient human behavior and settlement patterns. Imagine being able to see how ancient civilizations interacted with their environment, all through the lens of modern technology. That's the magic of GIS!
One of the most significant advantages of GIS is its ability to analyze spatial relationships. By layering various data sets—such as topography, soil types, and archaeological findings—researchers can identify patterns that were previously hidden. For example, GIS can reveal how the location of a settlement correlates with nearby water sources or trade routes, offering clues about the daily lives of ancient people. This analytical power allows archaeologists to ask questions like, "Where did they build their homes? Why here?" and uncover answers that contribute to our understanding of history.
Moreover, GIS is instrumental in mapping historical landscapes. By reconstructing these landscapes, researchers can visualize how ancient civilizations adapted to their surroundings over time. This process often involves comparing modern maps with archaeological data, allowing for a fascinating glimpse into the past. For instance, a GIS analysis might show how a river's course changed over centuries and how that shift influenced settlement patterns. Such insights are invaluable for understanding the dynamics of ancient societies.
Another critical application of GIS in archaeology is in site management and preservation. Archaeological sites are often at risk due to urban development, climate change, and other factors. GIS tools help archaeologists monitor these sites, track changes over time, and prioritize preservation efforts. By mapping the condition of various sites, researchers can make informed decisions about where to allocate resources for conservation. This proactive approach ensures that our cultural heritage is protected for future generations.
The integration of GIS with other technologies, such as remote sensing and 3D modeling, further enhances its capabilities. For example, when combined with satellite imagery, GIS can identify potential archaeological sites that may not be visible on the ground. This synergy between technologies creates a more comprehensive understanding of archaeological landscapes and improves the efficiency of research methodologies.
In conclusion, GIS is more than just a mapping tool; it is a transformative technology that has reshaped the way archaeologists conduct research. By providing insights into spatial relationships and historical contexts, GIS not only enhances our understanding of ancient cultures but also plays a vital role in the preservation of our shared heritage. As technology continues to evolve, the potential for GIS in archaeology is boundless, promising exciting discoveries that will further illuminate the stories of our past.
- What is GIS? GIS stands for Geographic Information Systems, a technology used to analyze and visualize spatial data.
- How does GIS benefit archaeology? GIS allows archaeologists to analyze spatial relationships, reconstruct historical landscapes, and manage site preservation effectively.
- Can GIS help in discovering new archaeological sites? Yes, by analyzing various data layers, GIS can identify potential excavation sites that may not be visible through traditional methods.
- Is GIS only used in archaeology? No, GIS is utilized in various fields, including urban planning, environmental science, and public health, among others.

Mapping Historical Landscapes
Mapping historical landscapes is like piecing together a giant puzzle where each piece reveals a story of how ancient civilizations interacted with their environment. Through the use of Geographic Information Systems (GIS), archaeologists have the remarkable ability to reconstruct these landscapes, shedding light on the intricate relationships between human activity and the natural world. Imagine standing in a field that was once bustling with life, where people farmed, traded, and built their homes. GIS technology allows researchers to visualize these past environments, giving us a glimpse into the lives of those who came before us.
One of the most fascinating aspects of mapping historical landscapes is the ability to analyze spatial relationships. By layering different types of data—such as topography, vegetation, and archaeological finds—archaeologists can identify patterns that reveal how ancient societies adapted to their surroundings. For instance, they can determine where settlements were established based on access to water sources or fertile land. This kind of analysis not only enhances our understanding of how ancient peoples lived but also informs us about their social structures and cultural practices.
Moreover, GIS enables researchers to visualize changes over time. By comparing historical maps with modern satellite imagery, they can track alterations in land use, climate, and environmental conditions. This temporal aspect is crucial; it helps to illustrate how civilizations responded to challenges such as droughts, floods, or invasions. For example, a study might reveal that a once-thriving city declined due to environmental degradation, prompting its inhabitants to migrate to more sustainable areas. Such insights are invaluable for understanding the dynamics of ancient societies and their resilience.
In addition to enhancing academic research, mapping historical landscapes has significant implications for cultural heritage management. By creating detailed maps of archaeological sites, archaeologists can prioritize areas for preservation and protection. This proactive approach is essential in today’s world, where urban development and climate change pose threats to these irreplaceable resources. Through GIS, we can advocate for the safeguarding of these sites, ensuring that future generations can experience and learn from our shared history.
To sum it up, mapping historical landscapes is not just about creating pretty pictures; it’s about unlocking the secrets of our past. The integration of GIS technology into archaeology has revolutionized how we study ancient cultures, providing us with tools to visualize, analyze, and ultimately understand the complex tapestry of human history. As technology continues to evolve, so too will our ability to explore and appreciate the landscapes of our ancestors.
- What is GIS and how is it used in archaeology? GIS, or Geographic Information Systems, is a technology that allows researchers to analyze spatial data and visualize historical landscapes, enhancing our understanding of ancient human behavior and environmental interactions.
- Why is mapping historical landscapes important? It helps archaeologists understand how ancient civilizations interacted with their environments, informs preservation efforts, and provides insights into social structures and cultural practices.
- How does GIS contribute to cultural heritage management? GIS allows for the creation of detailed maps of archaeological sites, helping to prioritize areas for preservation and protection against threats like urban development and climate change.

Site Management and Preservation
Effective site management and preservation are crucial components in the field of archaeology, ensuring that the remnants of our past are protected for future generations. With the advent of advanced technologies, archaeologists can now monitor and manage archaeological sites more efficiently than ever before. One of the primary tools that have revolutionized this process is Geographic Information Systems (GIS), which allows researchers to create detailed maps and models of archaeological sites. These tools enable the visualization of site layouts, helping to identify areas that are at risk from environmental factors or human activities.
Moreover, GIS technology provides a platform for analyzing changes over time, which is essential for preserving cultural heritage. By tracking alterations in site conditions, archaeologists can prioritize preservation efforts and allocate resources effectively. For instance, if a site shows signs of erosion or damage due to climate change, immediate action can be taken to mitigate these threats. This proactive approach not only safeguards the site but also enhances our understanding of how ancient civilizations interacted with their environments.
In addition to GIS, the integration of remote sensing technologies plays a vital role in site management. Techniques such as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) allow archaeologists to survey large areas quickly and accurately. This capability is particularly beneficial in dense forested regions where traditional excavation methods would be time-consuming and labor-intensive. By utilizing remote sensing, archaeologists can discover previously unknown sites and gather data without disturbing the land, promoting a more sustainable approach to archaeological research.
Collaboration with local communities is another essential aspect of effective site management. Engaging with those who live near archaeological sites can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility towards preserving cultural heritage. By involving local populations in preservation efforts, archaeologists can create educational programs that raise awareness about the significance of these sites. This not only helps protect the sites themselves but also enriches the community's understanding of their history.
To summarize, the combination of advanced technologies, GIS, remote sensing, and community involvement creates a robust framework for site management and preservation. By employing these tools and strategies, archaeologists can ensure that the stories of our ancestors continue to be told and appreciated, allowing future generations to connect with their cultural heritage.
- What is the role of GIS in archaeology?
GIS helps archaeologists analyze spatial relationships and patterns in archaeological data, enhancing our understanding of ancient human behavior and settlement patterns. - How does remote sensing benefit archaeological research?
Remote sensing technologies allow for the quick survey of large areas, revealing hidden structures without the need for extensive excavation. - Why is community involvement important in site preservation?
Engaging local communities fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, which is crucial for the long-term protection of archaeological sites. - What are the challenges of site management?
Challenges include environmental threats, urban development, and limited funding for preservation efforts.

Artificial Intelligence in Archaeology
Artificial intelligence (AI) is making waves in the world of archaeology, transforming how researchers analyze data and uncover the secrets of our past. Imagine having a super-smart assistant that can sift through mountains of information, identify patterns, and even predict where to dig next—sounds like something out of a sci-fi movie, right? But this is the reality we’re stepping into, and it’s reshaping the archaeological landscape. With AI, archaeologists can process large datasets faster and more accurately than ever before, enhancing the efficiency of their research and opening up new avenues for discovery.
One of the most exciting applications of AI in archaeology is machine learning, a branch of AI that enables computers to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. By feeding machine learning algorithms with vast amounts of archaeological data, researchers can uncover trends and relationships that might not be immediately obvious. For instance, these algorithms can analyze artifacts, settlement patterns, and even environmental data to provide insights into how ancient cultures interacted with their surroundings. This not only enriches our understanding of history but also allows archaeologists to make informed decisions about where to focus their excavation efforts.
Another groundbreaking application of AI is predictive modeling. This technique uses historical data to forecast where potential archaeological sites might be located. Think of it as a treasure map drawn by data! By analyzing factors such as past human behavior, environmental changes, and settlement patterns, predictive models can highlight areas that are more likely to yield significant finds. This is particularly valuable in regions where archaeological sites are sparse or where previous excavations have been unsuccessful. By honing in on promising locations, archaeologists can maximize their chances of uncovering new artifacts and sites of interest.
The integration of AI into archaeological practices isn’t just about efficiency; it’s also about collaboration. Interdisciplinary teamwork between archaeologists and computer scientists has led to innovative solutions that enhance research methodologies. For example, computer scientists can develop sophisticated algorithms that help archaeologists analyze satellite imagery or LiDAR data, identifying potential excavation sites that may have previously gone unnoticed. This collaboration is akin to a dynamic duo working together to crack a code—each bringing their unique skills to the table to unlock the mysteries of the past.
In conclusion, the role of artificial intelligence in archaeology is not just a passing trend; it’s a revolutionary shift that is transforming how we study ancient cultures. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more exciting developments in the field. From machine learning to predictive modeling, AI is not only enhancing our research capabilities but also enriching our understanding of human history. The future of archaeology is bright, and with AI by our side, the possibilities are endless.
- What is the role of AI in archaeology?
AI helps archaeologists analyze large datasets, identify patterns, and predict potential excavation sites, enhancing the efficiency of research. - How does machine learning benefit archaeological research?
Machine learning algorithms can uncover trends in archaeological data that may not be immediately apparent, providing deeper insights into ancient cultures. - What is predictive modeling in archaeology?
Predictive modeling uses historical data to forecast where archaeological sites might be located, helping archaeologists focus their excavation efforts. - Are there any challenges in using AI in archaeology?
Yes, challenges include the need for high-quality data, the complexity of algorithms, and ensuring that AI tools are accessible to archaeologists.

Machine Learning Applications
As we delve deeper into the world of archaeology, the integration of machine learning is proving to be a game-changer. Imagine having the ability to sift through mountains of data in the blink of an eye, uncovering patterns and insights that would take a human researcher years to identify. That's the magic of machine learning! By employing sophisticated algorithms, archaeologists can analyze vast datasets, revealing trends that are not readily apparent. For instance, machine learning can help in classifying artifacts based on their features, allowing researchers to organize and interpret findings more effectively.
One of the most exciting aspects of machine learning in archaeology is its potential for predictive modeling. This technique enables archaeologists to forecast where significant archaeological sites might be located based on historical data and environmental factors. By analyzing previous excavation sites, settlement patterns, and geographical features, machine learning models can highlight areas that are likely to yield new discoveries. This not only enhances the efficiency of archaeological surveys but also significantly increases the chances of finding important artifacts that could reshape our understanding of ancient cultures.
Moreover, machine learning is not just about finding new sites; it also plays a crucial role in data interpretation. With the ability to process and analyze complex datasets, machine learning algorithms can assist researchers in making connections between different pieces of information. For example, by correlating data from various excavation sites, researchers can gain insights into trade routes, social structures, and even climate impacts on ancient societies. This holistic approach is invaluable for reconstructing the past and understanding the intricate web of human history.
To illustrate the impact of machine learning, consider the following table that summarizes some key applications:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Artifact Classification | Using algorithms to categorize artifacts based on their physical characteristics. |
| Predictive Site Modeling | Forecasting potential excavation sites using historical and environmental data. |
| Data Correlation | Identifying relationships between different archaeological datasets to uncover new insights. |
In conclusion, the applications of machine learning in archaeology are vast and varied. As we continue to embrace these technological advancements, we are not only enhancing our research capabilities but also paving the way for a deeper understanding of our shared human heritage. The future of archaeology looks bright, and with machine learning at the helm, we are bound to make discoveries that will astonish us and future generations.
- What is machine learning in archaeology? Machine learning in archaeology refers to the use of algorithms and statistical models to analyze and interpret archaeological data, helping researchers identify patterns and make predictions.
- How does predictive modeling work? Predictive modeling uses historical data and machine learning techniques to forecast potential excavation sites, improving the efficiency of archaeological surveys.
- Can machine learning help in artifact preservation? Yes, by providing detailed analyses and classifications, machine learning can assist in the preservation and conservation of artifacts by ensuring they are handled and stored correctly.

Predictive Modeling
Predictive modeling in archaeology is like having a crystal ball that helps researchers look into the past and uncover the mysteries of ancient civilizations. By utilizing historical data, archaeologists can make educated guesses about where significant archaeological sites might be located. This technique has revolutionized the way fieldwork is conducted, significantly increasing the likelihood of successful excavations. Imagine walking through a landscape, equipped with data that points you toward hidden treasures buried beneath the earth. That’s the power of predictive modeling!
At its core, predictive modeling involves the use of advanced algorithms and statistical techniques to analyze patterns in existing archaeological data. For instance, researchers might look at the locations of previously discovered sites, environmental factors, and ancient settlement patterns to create a model that predicts where other sites could be found. This approach not only saves time and resources but also enhances the overall efficiency of archaeological research.
One of the most exciting aspects of predictive modeling is its ability to process vast amounts of data quickly. With the help of machine learning and sophisticated software, archaeologists can identify trends and correlations that would be nearly impossible to discern through manual analysis alone. For example, a predictive model might reveal that ancient settlements were often located near water sources, leading researchers to prioritize excavation efforts in those areas.
In practice, predictive modeling involves several key steps:
- Data Collection: Gathering existing archaeological data, including site locations, artifacts, and environmental conditions.
- Data Analysis: Using statistical methods to analyze the collected data and identify patterns.
- Model Development: Creating a predictive model based on the analyzed data to forecast potential site locations.
- Field Testing: Conducting excavations in areas identified by the model to verify its accuracy.
As predictive modeling continues to evolve, its applications in archaeology are becoming even more sophisticated. For instance, researchers are now incorporating geospatial analysis into their models, allowing them to account for geographic and environmental variables that influence human settlement. This holistic approach not only aids in predicting the location of archaeological sites but also provides insights into the socio-economic factors that shaped ancient communities.
Ultimately, the integration of predictive modeling into archaeological practice is not just about finding artifacts; it's about weaving together the threads of human history. It allows archaeologists to tell stories of ancient peoples, their interactions with the environment, and their cultural evolution. As technology continues to advance, the potential for predictive modeling in archaeology will likely expand, leading to even more groundbreaking discoveries and a deeper understanding of our shared past.
- What is predictive modeling in archaeology?
Predictive modeling is a technique used by archaeologists to forecast the locations of potential archaeological sites based on existing data and patterns. - How does predictive modeling improve archaeological research?
It enhances efficiency by identifying promising excavation sites, saving time and resources, and increasing the likelihood of successful discoveries. - What types of data are used in predictive modeling?
Data can include historical site locations, environmental factors, artifact distributions, and settlement patterns. - Can predictive modeling be combined with other technologies?
Yes, it is often integrated with GIS and machine learning to provide more accurate predictions and insights into ancient human behavior.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How has technology changed archaeological practices?
Technology has revolutionized archaeological practices by introducing tools like remote sensing, 3D modeling, and GIS. These advancements allow archaeologists to survey large areas quickly, visualize artifacts, and analyze spatial data, enhancing both research efficiency and accuracy.
- What is remote sensing, and how is it used in archaeology?
Remote sensing involves technologies such as LiDAR and satellite imagery that enable archaeologists to survey landscapes from above. This method reveals hidden structures and sites without the need for extensive digging, saving time and resources while uncovering historical treasures.
- What are the benefits of 3D modeling in archaeology?
3D modeling allows for the digital recreation of artifacts and archaeological sites, providing immersive experiences for researchers and the public. It enhances understanding of historical contexts and preserves artifacts for future study without physical handling.
- How does GIS contribute to archaeological research?
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) help archaeologists analyze spatial relationships within archaeological data. This technology aids in reconstructing historical landscapes and managing sites, providing insights into ancient human behavior and environmental interactions.
- What role does artificial intelligence play in archaeology?
Artificial intelligence is transforming archaeology by analyzing large datasets, identifying patterns, and predicting potential excavation sites. Machine learning algorithms enhance the understanding of ancient cultures by uncovering trends that may not be visible to human researchers.
- Can you explain photogrammetry and its significance?
Photogrammetry is a technique that creates accurate 3D models from photographs. It’s significant for detailed analysis and preservation of artifacts, allowing researchers to study and restore items without risking damage to delicate materials.
- How does technology enhance public engagement with archaeology?
Through 3D models and virtual tours, technology makes archaeological findings more accessible to the public. These tools provide educational resources that engage wider audiences, fostering a greater appreciation for archaeological discoveries and cultural heritage.