How to Conduct Research on Human-Animal Interactions
Researching the intricate tapestry of human-animal interactions is a fascinating endeavor that requires a thoughtful approach. This field of study is not just about observing animals in their habitats or noting how people interact with their pets; it encompasses a wide variety of contexts, including therapy, conservation, and companionship. Understanding these interactions can reveal profound insights into the psychological, social, and economic implications that shape our relationships with animals. Imagine the bond between a therapy dog and a patient—a relationship that can transform lives and offer healing in ways words cannot describe. In this article, we will explore the methodologies and considerations essential for conducting effective research in this captivating field.
At its core, human-animal interaction refers to the various ways in which humans and animals engage with each other. These interactions can range from the simple companionship of a pet to complex relationships that involve emotional support, conservation efforts, and even economic exchanges. The significance of these relationships cannot be overstated; studies have shown that animals can provide emotional support, reduce stress, and even improve overall mental health. Furthermore, the economic impact of human-animal interactions, particularly in sectors like therapy and conservation, underscores the need for comprehensive research. For instance, therapy animals are increasingly utilized in hospitals and schools, showcasing just how vital these relationships can be.
When it comes to studying human-animal interactions, selecting the right research methodology is crucial. Researchers typically employ two primary approaches: qualitative and quantitative methods. Each has its strengths and can provide valuable insights into different aspects of these interactions. For example, qualitative methods like interviews and focus groups can delve deep into personal narratives, while quantitative methods such as surveys and experiments can uncover patterns and correlations. The choice of methodology should align with the specific research questions being posed, as this alignment is key to obtaining meaningful results.
Qualitative research methods offer a window into the emotional and social dimensions of human-animal relationships. Techniques like interviews and focus groups allow researchers to gather rich, descriptive data that reflects personal experiences and perceptions. This approach can unveil the underlying feelings people have towards animals, revealing how these bonds influence their lives. For instance, a study involving pet owners might explore how their pets contribute to their sense of well-being and happiness, painting a vivid picture of the emotional landscape of human-animal interactions.
Case studies serve as a powerful tool for examining specific instances of human-animal interaction. By focusing on unique contexts, researchers can draw broader conclusions about the dynamics at play. For example, a case study on therapy animals in a particular hospital could highlight how these animals impact patient recovery rates, shedding light on the potential benefits of incorporating animals into healthcare settings. Such detailed examinations provide invaluable insights that can inform future research and practice.
Another qualitative method, ethnographic research, involves immersive observation of human-animal interactions in natural settings. This approach allows researchers to collect rich, contextual data that captures the complexities of these relationships in everyday life. Imagine observing a family interacting with their dog during a picnic; the nuances of their communication, the joy in their play, and the comfort in their companionship all contribute to a deeper understanding of the bond between humans and animals.
On the flip side, quantitative research methods utilize statistical analysis to uncover patterns and correlations in human-animal interactions. Techniques such as surveys and controlled experiments can help researchers identify causal relationships, offering a more objective view of these interactions. For example, a large-scale survey could reveal trends in pet ownership and its correlation with mental health outcomes, providing data-driven insights that can influence public policy and community programs.
When conducting research on human-animal interactions, ethical considerations are paramount. Researchers must navigate complex issues related to consent, welfare, and the potential impacts of their findings on both human and animal participants. Ensuring that the welfare of animal subjects is prioritized is critical; this requires strict adherence to ethical guidelines that consider the physical and psychological well-being of the animals involved.
Ensuring the welfare of animal subjects is not just a legal requirement; it is a moral imperative. Researchers must be vigilant in their efforts to uphold ethical standards, ensuring that animals are treated with respect and care throughout the research process. This includes providing appropriate living conditions, minimizing stress, and considering the emotional needs of the animals involved.
In addition to animal welfare, obtaining informed consent from human participants is essential. This process ensures that participants understand the research purpose, procedures, and potential risks, fostering trust and transparency. Clear communication is key; researchers should take the time to explain the study and address any questions participants may have, thereby enhancing the integrity of the research.
Once data is collected, the next step is analysis. Various techniques can be employed depending on whether the data is qualitative or quantitative. For quantitative data, statistical methods such as regression analysis and ANOVA are crucial for interpreting relationships between variables. On the other hand, thematic analysis provides a framework for analyzing qualitative data, allowing researchers to identify patterns and themes in participant responses. Both approaches are vital for enriching our understanding of human-animal relationships.
Statistical methods enable researchers to draw meaningful conclusions from quantitative data. By employing techniques such as regression analysis, researchers can explore how different variables interact within human-animal interactions. For instance, a study might examine how the frequency of pet ownership correlates with reported levels of happiness, providing valuable insights that can inform future research and practice.
Thematic analysis is particularly effective for qualitative data, allowing researchers to identify recurring themes and patterns in participant responses. This analysis can reveal profound insights into how people perceive their relationships with animals, ultimately enriching the understanding of these complex interactions. For example, a thematic analysis of interviews with therapy animal handlers might uncover common themes related to emotional fulfillment and the transformative power of these relationships.
The implications of research on human-animal interactions are far-reaching. Findings can inform public policy, enhance community programs, and ultimately improve the welfare of both humans and animals. For instance, research insights can guide the development of policies that promote animal welfare in various settings, ensuring that animals are treated with respect and dignity.
Research findings can play a pivotal role in shaping policy decisions. By providing evidence-based recommendations, researchers can advocate for practices that enhance animal welfare and improve human experiences with animals. This can lead to the implementation of policies that support the integration of therapy animals into healthcare systems or promote responsible pet ownership.
Moreover, insights from research can guide the development of community programs that foster positive human-animal interactions. Initiatives such as therapy animal programs, educational outreach, and conservation efforts can benefit from research findings, ultimately enhancing the quality of life for both humans and animals. Imagine a community where therapy animals are regularly integrated into schools, providing emotional support to students—this is the kind of impact research can have.
- What are human-animal interactions?
Human-animal interactions refer to the various ways in which humans and animals engage with each other, encompassing companionship, therapy, and conservation. - Why is research on human-animal interactions important?
Understanding these interactions can lead to insights that improve animal welfare, inform public policy, and enhance community programs. - What methodologies are used in this research?
Both qualitative and quantitative methods are used, including interviews, surveys, and observational studies. - What ethical considerations should be taken into account?
Researchers must prioritize animal welfare, obtain informed consent from human participants, and adhere to ethical guidelines throughout the research process.

Understanding Human-Animal Interaction
Human-animal interactions are a fascinating tapestry woven from the threads of companionship, emotional support, and mutual benefit. These interactions are not just limited to pets and their owners; they extend to various contexts, including therapy, conservation efforts, and even agricultural settings. The significance of these relationships cannot be overstated, as they impact our psychological well-being, social structures, and economic landscapes.
At the heart of these interactions lies the psychological connection that many people experience with animals. For instance, studies have shown that pet ownership can lead to reduced levels of stress and anxiety, offering a sense of companionship that is often hard to find in human relationships. Imagine coming home after a long day, greeted by a wagging tail or a gentle purr. This simple act can elevate mood, providing a sense of belonging and emotional comfort.
Moreover, human-animal interactions play a crucial role in therapy settings. Animal-assisted therapy has gained traction in recent years, where trained animals help individuals cope with various mental health challenges. The presence of an animal can facilitate communication, encourage physical activity, and promote emotional healing. For example, therapy dogs are increasingly used in hospitals and schools, providing comfort to patients and students alike. This highlights the profound impact that animals can have on our lives, often serving as catalysts for positive change.
From an economic perspective, the bond between humans and animals can also lead to significant benefits. The pet industry alone is a multi-billion dollar market, encompassing everything from food and toys to veterinary care and grooming services. Additionally, animals contribute to agriculture by providing labor and companionship to farmers, enhancing productivity and emotional well-being in rural communities.
In the realm of conservation, understanding human-animal interactions is vital for protecting endangered species and their habitats. By fostering a sense of appreciation and responsibility towards wildlife, we can encourage sustainable practices that benefit both humans and animals. For instance, community programs that promote wildlife education can lead to more informed and engaged citizens who advocate for conservation efforts.
Ultimately, the significance of human-animal interactions is multifaceted, influencing our emotional health, societal norms, and economic activities. As we delve deeper into the study of these interactions, we uncover the rich layers that define our relationships with animals, revealing how intertwined our lives truly are.
- What are some benefits of human-animal interactions? Human-animal interactions can improve mental health, reduce stress, and promote social connections.
- How does animal-assisted therapy work? Animal-assisted therapy involves trained animals helping individuals cope with emotional and psychological challenges.
- What role do animals play in conservation? Animals help raise awareness about environmental issues and can be key players in conservation efforts.

Research Methodologies
When it comes to studying the intricate tapestry of human-animal interactions, selecting the right research methodology is crucial. The methodologies can be broadly categorized into two main types: qualitative and quantitative. Each approach offers unique insights and advantages, depending on the specific research questions being posed. By understanding the strengths and limitations of these methodologies, researchers can tailor their studies to effectively capture the nuances of the relationships between humans and animals.
Qualitative research methods are particularly valuable when delving into the emotional and subjective experiences of individuals. These methods encompass a variety of techniques, such as interviews, focus groups, and open-ended surveys. For instance, interviews allow participants to share their narratives and feelings towards their pets or other animals in their lives, providing a rich, textured understanding of the human-animal bond. Similarly, focus groups can facilitate dynamic discussions, revealing shared experiences and diverse perspectives among participants. This approach often uncovers themes related to companionship, emotional support, and the therapeutic benefits of animals, which quantitative methods might overlook.
On the other hand, quantitative research employs structured methods that enable researchers to gather numerical data and perform statistical analyses. This could involve surveys with closed-ended questions designed to quantify attitudes or behaviors regarding animals. For example, a survey might ask participants to rate their agreement with statements about the benefits of animal companionship on a scale of 1 to 5. Such data can be analyzed using statistical techniques like regression analysis to identify correlations between variables, such as the frequency of pet ownership and reported levels of happiness.
To illustrate the differences between qualitative and quantitative methodologies, consider the following table:
| Methodology | Characteristics | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Qualitative | Exploratory, subjective, rich in detail | Interviews, focus groups, ethnographic studies |
| Quantitative | Structured, objective, statistical analysis | Surveys, experiments, observational studies |
Both methodologies can complement each other, creating a more holistic understanding of human-animal interactions. For instance, a researcher might start with qualitative interviews to explore themes and then develop a quantitative survey based on those insights to test hypotheses on a larger scale.
Ultimately, the choice of methodology should align with the research objectives and the questions being asked. By carefully considering the appropriate methods, researchers can contribute valuable knowledge about the complex and rewarding relationships between humans and animals, paving the way for improved welfare and understanding for both species.
- What is the main difference between qualitative and quantitative research? Qualitative research focuses on understanding subjective experiences and emotions, while quantitative research seeks to quantify data and identify patterns through statistical analysis.
- Why is it important to choose the right research methodology? The right methodology ensures that the research questions are effectively addressed, leading to more accurate and meaningful findings.
- Can qualitative and quantitative methods be used together? Yes, using both methods in a mixed-methods approach can provide a more comprehensive understanding of human-animal interactions.

Qualitative Approaches
When it comes to studying the intricate tapestry of human-animal interactions, shine a light on the emotional and social dimensions that often get lost in the numbers. These methods dig deep, allowing researchers to explore the nuanced experiences and perceptions that individuals hold about their relationships with animals. Imagine sitting down for a chat with someone about their beloved pet; the stories, emotions, and insights shared can paint a vivid picture that statistics alone cannot capture.
One of the most effective qualitative methods is the interview. Through one-on-one conversations, researchers can gather rich, detailed narratives that reveal how people perceive their bonds with animals. For instance, an interview with a therapy animal handler can uncover not just the practical benefits of their work but also the profound emotional connections that develop between the handler, the animal, and the individuals they assist. This method opens up a world of understanding, allowing researchers to grasp the depth of feelings and experiences that define these interactions.
Another powerful qualitative approach is the use of focus groups. By bringing together a diverse group of participants, researchers can facilitate discussions that elicit a range of perspectives. This method is particularly useful in exploring community attitudes towards animals, such as the role of pets in families or the impact of wildlife conservation efforts. Participants can bounce ideas off each other, sparking insights that might not emerge in individual interviews. It’s like a brainstorming session where the collective wisdom of the group can lead to unexpected revelations.
In addition to interviews and focus groups, case studies provide a unique lens through which to examine human-animal interactions. By focusing on specific instances, researchers can delve into the details of particular relationships, uncovering the factors that contribute to their success or challenges. For example, a case study might explore a successful therapy program that pairs trained dogs with veterans suffering from PTSD, highlighting the transformative effects on both the animals and the humans involved. This method not only adds depth to the research but also allows for the exploration of unique contexts that can inform broader conclusions about the dynamics at play.
Moreover, ethnographic research takes qualitative analysis a step further by immersing researchers in the environments where human-animal interactions occur. This method involves observing interactions in real-time, providing a rich, contextual understanding of how these relationships unfold in everyday life. Imagine a researcher spending time at a local animal shelter, witnessing the connections that form between volunteers and animals. Ethnography captures the subtleties of behavior, communication, and emotional exchange that might otherwise go unnoticed, offering a holistic view of the human-animal bond.
In summary, qualitative approaches are invaluable for uncovering the intricate layers of human-animal interactions. By employing methods such as interviews, focus groups, case studies, and ethnographic research, scholars can gain insights that are not only rich in detail but also deeply meaningful. These approaches remind us that behind every statistic is a story waiting to be told, a connection yearning to be understood. As we delve deeper into these methodologies, we not only enhance our knowledge but also foster a greater appreciation for the profound relationships that exist between humans and animals.
- What are qualitative approaches in research?
Qualitative approaches are research methods that focus on understanding the meanings, experiences, and perspectives of individuals. They often involve collecting non-numerical data through interviews, focus groups, and observations. - Why are qualitative methods important in studying human-animal interactions?
These methods provide rich, detailed insights into the emotional and social dimensions of relationships between humans and animals, which quantitative methods may overlook. - How do interviews differ from focus groups?
Interviews are one-on-one conversations that allow for deep exploration of individual experiences, while focus groups involve discussions among a group of participants, fostering interaction and diverse perspectives. - What is the role of case studies in qualitative research?
Case studies offer an in-depth examination of specific instances of human-animal interaction, allowing researchers to draw broader conclusions about the dynamics involved.
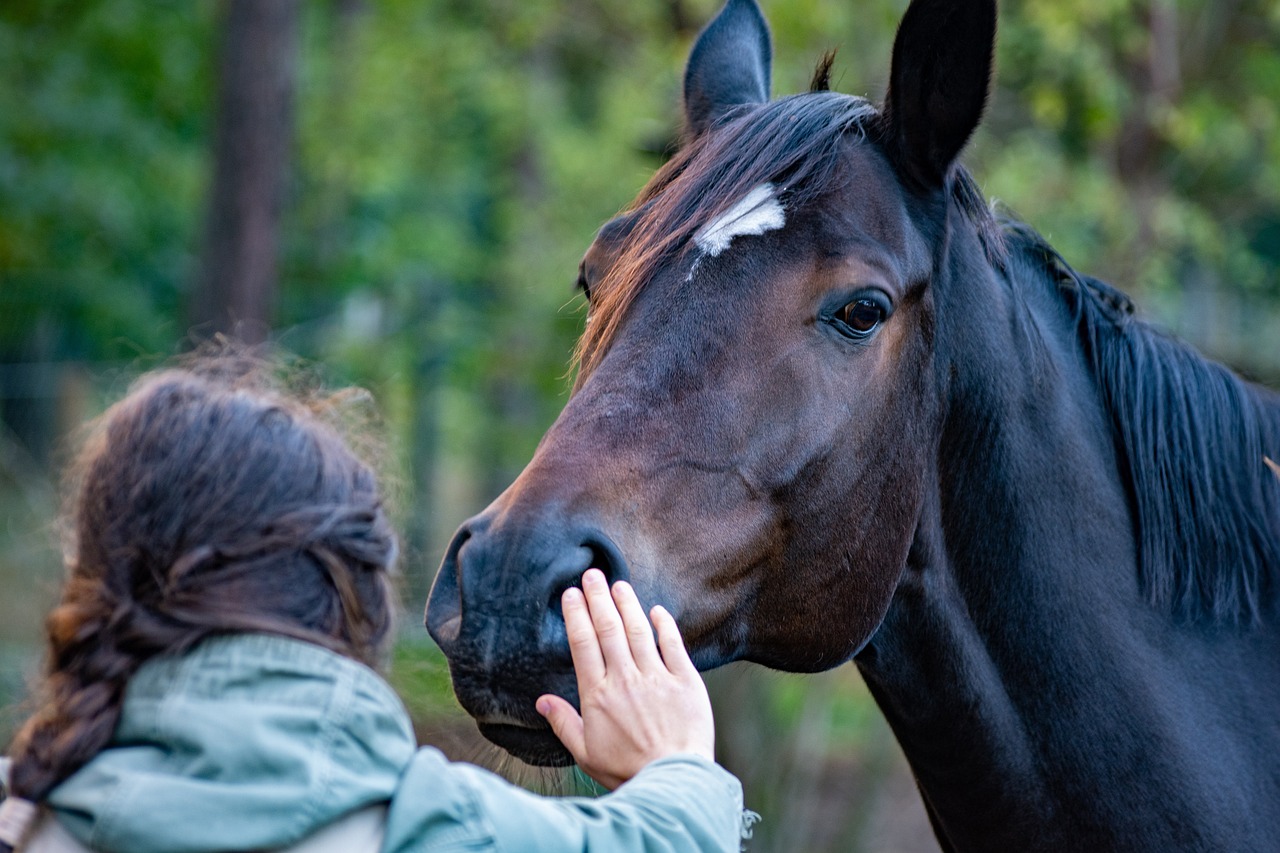

Case Studies
Case studies serve as a powerful tool in understanding the nuanced dynamics of human-animal interactions. By focusing on specific instances, researchers can delve deep into the complexities that characterize these relationships. For example, consider a case study involving therapy dogs in a hospital setting. Researchers observed how the presence of these animals impacted the emotional well-being of patients. The findings revealed that patients who interacted with therapy dogs reported lower levels of anxiety and enhanced feelings of comfort, showcasing the profound emotional connections that can be fostered between humans and animals.
Another compelling case study might explore the interactions between farmers and their livestock. This research could highlight how these relationships are not merely transactional but are built on trust and mutual understanding. Farmers often develop a bond with their animals, which can lead to better care practices and improved animal welfare. Such insights are invaluable, as they emphasize the importance of emotional connections in agricultural settings, ultimately influencing practices that benefit both the animals and the farmers.
Through these case studies, researchers can also identify broader trends and themes that emerge across different contexts. For instance, a recurring theme might be the role of animals in reducing social isolation among elderly populations. By examining various case studies that focus on this aspect, researchers can accumulate a wealth of information that underscores the potential benefits of human-animal interactions in enhancing quality of life.
To effectively present the findings of case studies, researchers often utilize tables to summarize key data points. Below is an example table that outlines different case studies and their primary findings:
| Case Study | Context | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Therapy Dogs in Hospitals | Healthcare | Reduced patient anxiety and increased comfort levels. |
| Farmers and Livestock | Agriculture | Stronger emotional bonds lead to better animal welfare practices. |
| Companionship for the Elderly | Community | Enhanced quality of life through reduced social isolation. |
In conclusion, case studies are invaluable in the field of human-animal interaction research. They provide rich, contextual insights that quantitative data alone may overlook. By examining specific instances, researchers can draw broader conclusions about the emotional, social, and economic implications of these interactions, ultimately contributing to a deeper understanding of the complex relationships between humans and animals.
- What is the purpose of case studies in human-animal interaction research?
Case studies allow researchers to explore specific instances of human-animal relationships in depth, revealing insights that broader studies may miss. - How do case studies contribute to animal welfare?
By highlighting positive interactions, case studies can inform better practices and policies that enhance animal welfare. - Can case studies influence public policy?
Absolutely! Findings from case studies can be used to advocate for policies that support better human-animal interactions.

Ethnographic Research
Ethnographic research is a fascinating approach that dives deep into the everyday lives of individuals and their interactions with animals. Unlike traditional research methods that may rely heavily on surveys or experiments, ethnography allows researchers to immerse themselves in the environment where these interactions occur. Imagine being a fly on the wall, observing the subtleties of human-animal relationships as they unfold in real-time. This method provides rich, contextual insights that are often missed in more structured research designs.
One of the most significant advantages of ethnographic research is its ability to capture the nuances and complexities of human-animal interactions. For instance, researchers may observe how a therapy dog interacts with patients in a hospital setting, noting not just the behaviors but also the emotional responses of both the animal and the human participants. This approach can reveal profound insights into the therapeutic benefits of such interactions, showcasing how they can alleviate anxiety, improve mood, and foster connections.
In conducting ethnographic research, researchers often engage in participant observation, where they become part of the community they are studying. This might involve spending extended periods with animal caretakers, veterinarians, or even families with pets. Through this immersive technique, researchers can gather data on various dimensions of human-animal interactions, such as:
- The emotional bonds formed between humans and animals
- The roles animals play in human social structures
- How cultural beliefs influence perceptions of animals
Moreover, ethnographic research often includes informal interviews and discussions, allowing researchers to gain a deeper understanding of the motivations and feelings that drive these interactions. By capturing personal stories and experiences, this method can highlight the transformative power of human-animal bonds, illustrating how they contribute to well-being, companionship, and even social change.
However, conducting ethnographic research is not without its challenges. It requires a significant time investment and a commitment to understanding the cultural contexts in which these interactions occur. Researchers must navigate ethical considerations carefully, ensuring that they respect the privacy and welfare of both human and animal participants. This balance between observation and ethical responsibility is crucial in producing credible and respectful research outcomes.
In summary, ethnographic research stands out as a powerful tool for studying human-animal interactions. By providing a window into the daily lives and emotional landscapes of those involved, it enriches our understanding of these unique relationships and their broader implications for society. As we continue to explore the intricacies of human-animal dynamics, ethnography will undoubtedly play a vital role in shaping our knowledge and appreciation of these connections.
Q1: What is ethnographic research?
A1: Ethnographic research is a qualitative research method that involves immersive observation and participation within a community to understand their behaviors, interactions, and cultural practices, particularly in the context of human-animal relationships.
Q2: How does ethnographic research differ from other research methods?
A2: Unlike surveys or experiments, ethnographic research focuses on real-life contexts and interactions, allowing researchers to capture the emotional and social nuances of human-animal relationships through direct observation and engagement.
Q3: What are some challenges of conducting ethnographic research?
A3: Challenges include the time commitment required for immersion, navigating ethical considerations regarding participant welfare, and ensuring accurate representation of the community being studied.
Q4: Why is ethnographic research important in studying human-animal interactions?
A4: It provides deep insights into the complexities of these relationships, revealing how they impact emotional well-being, social connections, and cultural perceptions of animals.

Quantitative Approaches
When it comes to studying human-animal interactions, offer a structured way to gather and analyze data. These methods are particularly useful for identifying patterns and establishing relationships between variables. For instance, researchers might use surveys to gather responses from pet owners about their experiences and perceptions regarding their animals. This data can then be analyzed statistically to uncover trends that might not be immediately apparent through qualitative observations.
One of the most common quantitative methods is the use of surveys. Surveys can be designed to include a range of question types, such as multiple-choice, Likert scales, and open-ended questions. By using diverse question formats, researchers can collect rich data that captures both the breadth and depth of human-animal interactions. For example, a survey might ask participants to rate their satisfaction with their pets on a scale from 1 to 10, while also allowing them to provide comments on their experiences. This combination of quantitative ratings and qualitative feedback creates a comprehensive dataset for analysis.
Another powerful quantitative method is the experimental design. In this approach, researchers manipulate one or more variables to observe the effects on human-animal interactions. For example, an experiment could involve varying the amount of time spent with a therapy animal and measuring the impact on participants' stress levels. By controlling for other variables, researchers can draw clearer conclusions about causation rather than mere correlation.
To ensure the validity of their findings, researchers often employ statistical techniques such as regression analysis or ANOVA (Analysis of Variance). These methods help to identify significant relationships and differences within the data. For instance, a regression analysis might reveal that individuals who spend more time with their pets report higher levels of happiness, while ANOVA could show differences in stress reduction between various types of therapy animals.
In summary, quantitative approaches provide a robust framework for studying human-animal interactions. By employing surveys and experimental designs, researchers can gather data that not only enhances our understanding of these complex relationships but also informs practices that can improve the well-being of both humans and animals.
- What are quantitative approaches in research?
Quantitative approaches involve collecting numerical data that can be analyzed statistically to identify patterns and relationships. - How do surveys contribute to understanding human-animal interactions?
Surveys gather structured responses from participants, providing insights into their experiences and perceptions regarding their interactions with animals. - What is the importance of experimental design in this research?
Experimental design allows researchers to manipulate variables and observe effects, helping to establish causation rather than mere correlation. - What statistical methods are commonly used in quantitative research?
Common methods include regression analysis and ANOVA, which help interpret the data and draw meaningful conclusions.

Ethical Considerations
When embarking on research related to human-animal interactions, it is crucial to navigate the complex landscape of . This field of study often involves both human and animal participants, necessitating a careful balance of interests and welfare. At the forefront of these considerations is the need to ensure that both human and animal subjects are treated with respect and dignity. Researchers must be vigilant about the potential impacts of their studies, ensuring that they do not inadvertently cause harm or distress.
One of the primary ethical concerns is animal welfare. Researchers must adhere to strict ethical guidelines designed to protect the physical and psychological well-being of animals involved in studies. This includes providing adequate care and minimizing any stress or discomfort that might arise during research activities. For instance, when studying therapy animals, it is essential to assess their emotional state and take steps to ensure they are not overworked or subjected to stressful environments. The following table outlines key ethical principles regarding animal welfare:
| Principle | Description |
|---|---|
| Respect for Life | Recognizing the intrinsic value of all living beings. |
| Minimization of Harm | Aiming to reduce any potential suffering of animal subjects. |
| Proper Care | Ensuring animals receive proper treatment and care throughout the study. |
Another critical aspect of ethical research is obtaining informed consent from human participants. This process involves providing clear and comprehensive information about the research purpose, procedures, and potential risks. It is essential that participants fully understand what they are consenting to, which fosters trust and transparency in the research process. Researchers should be prepared to answer any questions participants may have and ensure that they feel comfortable with their involvement. This can often be achieved through detailed consent forms and open dialogue before the study begins.
Moreover, researchers should consider the implications of their findings on both species involved. The outcomes of human-animal interaction studies can influence public policy, animal welfare practices, and community programs. Thus, it is vital to approach research with a mindset that prioritizes the well-being of both humans and animals, ensuring that the knowledge gained is used responsibly and ethically.
In summary, ethical considerations in human-animal interaction research encompass a range of factors, including animal welfare, informed consent, and the broader implications of research findings. By adhering to ethical principles, researchers can contribute to a deeper understanding of these complex relationships while promoting welfare and respect for all participants involved.
- What are the key ethical principles in human-animal interaction research? The key principles include respect for life, minimization of harm, and proper care of animal subjects.
- How can researchers ensure informed consent? Researchers can ensure informed consent by providing clear information about the study and addressing any questions participants may have.
- Why is animal welfare important in research? Animal welfare is crucial to prevent suffering and ensure ethical treatment, which reflects on the validity and reliability of research findings.

Animal Welfare
When it comes to conducting research on human-animal interactions, is a critical concern that cannot be overlooked. Ensuring the well-being of animal subjects is not just a legal obligation but a moral imperative that underscores the integrity of the research process. Researchers must adhere to strict ethical guidelines that prioritize the physical and psychological health of the animals involved. This includes providing proper housing, nutrition, and care to the animals, as well as minimizing any stress or discomfort they may experience during the study.
Moreover, it is essential to recognize that animals are sentient beings capable of experiencing a range of emotions. This awareness compels researchers to design studies that are not only scientifically sound but also compassionate. For instance, if an experiment involves training animals, researchers should use positive reinforcement techniques rather than punitive measures, fostering a more humane approach to animal training.
In addition to direct care, researchers should also consider the broader implications of their work on animal welfare. This includes understanding how their findings may influence public perceptions of animals and animal rights. For example, if research suggests that certain species thrive better in specific environments, it could lead to better habitat management practices and conservation efforts. Thus, the ripple effects of ethical research can extend far beyond the immediate study, impacting animal welfare on a larger scale.
To further illustrate the importance of animal welfare in research, consider the following key principles:
- Respect for Animals: Recognizing and honoring the intrinsic value of animal life.
- Minimization of Harm: Designing studies to reduce any potential pain or distress to animal subjects.
- Transparency: Being open about research methods and findings to promote trust and accountability.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to established laws and guidelines that govern animal research.
By integrating these principles into research design, scientists can ensure that their work not only contributes to our understanding of human-animal interactions but also upholds the highest standards of animal welfare.
Ultimately, the goal of any research involving animals should be to advance knowledge while simultaneously enhancing the lives of the animals involved. This dual focus on scientific inquiry and ethical responsibility creates a framework where both humans and animals can thrive, aligning with the broader mission of fostering positive human-animal relationships.
Q: Why is animal welfare important in research?
A: Animal welfare is crucial in research to ensure the ethical treatment of animals, promote valid scientific results, and maintain public trust in research practices.
Q: What are some ethical guidelines for animal research?
A: Ethical guidelines typically include minimizing harm, ensuring proper care, obtaining informed consent from human participants, and adhering to regulatory standards.
Q: How can researchers ensure animal welfare during studies?
A: Researchers can ensure animal welfare by providing appropriate housing and care, using humane training methods, and designing studies to minimize stress and discomfort.

Informed Consent
Informed consent is a fundamental principle in research, particularly when it involves human participants. It serves as a safeguard for participants, ensuring they are fully aware of what their involvement entails. Imagine stepping into a new world where your participation could influence the lives of both humans and animals; wouldn't you want to know exactly what that means? Informed consent is not just a formality; it is a crucial process that fosters trust and transparency between researchers and participants.
To obtain informed consent, researchers must clearly communicate several key elements to potential participants:
- Purpose of the Study: Participants should understand why the research is being conducted and what the researchers hope to achieve.
- Procedures Involved: It's essential to outline what participation entails, including any tasks or activities participants will engage in.
- Potential Risks and Benefits: Participants need to be informed of any risks associated with their involvement, as well as any potential benefits they may receive.
- Confidentiality Assurance: Researchers must explain how they will protect participants' privacy and the measures in place to maintain confidentiality.
- Right to Withdraw: Participants should know they have the right to withdraw from the study at any point without any negative consequences.
By addressing these elements, researchers can create a comprehensive informed consent process that respects the autonomy of participants. This process is particularly vital in studies involving sensitive topics or vulnerable populations, as it ensures participants are not only informed but also empowered to make choices about their involvement.
Moreover, the informed consent process should be ongoing, meaning that if any new information arises during the study that could affect participants' willingness to continue, they should be informed immediately. This dynamic approach reinforces the ethical commitment of researchers to prioritize the well-being of their participants, enhancing the overall integrity of the research.
In summary, informed consent is a cornerstone of ethical research practices. It not only protects participants but also enhances the credibility of the research findings. By fostering an environment of trust and transparency, researchers can ensure that their studies on human-animal interactions are conducted ethically, ultimately benefiting both species involved.
- What is informed consent? Informed consent is the process of providing potential research participants with clear and comprehensive information about a study, allowing them to make an informed decision about their participation.
- Why is informed consent important? It protects participants' rights, ensures ethical standards are upheld, and fosters trust between researchers and participants.
- Can participants withdraw from a study? Yes, participants have the right to withdraw from a study at any time without facing negative consequences.
- What information should be included in the informed consent process? Key elements include the purpose of the study, procedures involved, potential risks and benefits, confidentiality assurances, and the right to withdraw.

Data Analysis Techniques
When it comes to understanding the intricate dynamics of human-animal interactions, play a pivotal role. These techniques help researchers sift through the vast amounts of data collected during studies, allowing them to draw meaningful conclusions and insights. In this section, we will explore various methods that are particularly effective in analyzing both qualitative and quantitative data.
For quantitative research, statistical methods are essential. They provide a framework for interpreting numerical data, helping researchers to identify trends, correlations, and even causal relationships. Some of the most commonly used statistical techniques include:
- Regression Analysis: This method helps to understand the relationship between dependent and independent variables, allowing researchers to predict outcomes based on certain inputs.
- ANOVA (Analysis of Variance): ANOVA is used to compare means across different groups, which is particularly useful in studies that involve multiple animal species or varying human interactions.
- Chi-Square Tests: This non-parametric test is great for examining the association between categorical variables, making it useful for studies that categorize human-animal interactions.
On the other hand, qualitative research requires a different approach to data analysis. Thematic analysis is one of the most widely used techniques in this realm. It allows researchers to identify and analyze patterns within qualitative data, such as interview transcripts or open-ended survey responses. The process involves several key steps:
- Familiarization: Researchers immerse themselves in the data to understand the depth and breadth of the content.
- Generating Initial Codes: Key points of interest are coded to facilitate easier analysis.
- Searching for Themes: Codes are grouped into broader themes that capture the essence of the data.
- Reviewing Themes: Themes are evaluated and refined to ensure they accurately represent the data.
- Defining and Naming Themes: Each theme is clearly defined and named, providing clarity in the analysis.
Both statistical and thematic analyses are crucial for drawing robust conclusions from research on human-animal interactions. They not only help in understanding the data but also in shaping future research questions and methodologies. The insights gained from these analyses can lead to significant advancements in animal welfare practices, public policy, and community outreach programs.
As we move forward, it is essential to remember that the integrity of the analysis hinges on the quality of the data collected. Thus, researchers must ensure that their data collection methods are sound and that they adhere to ethical standards throughout the research process.
1. What are the main differences between qualitative and quantitative research methods?
Qualitative research focuses on understanding human experiences and perceptions, often through interviews and observations, while quantitative research relies on numerical data and statistical analysis to identify patterns and relationships.
2. Why is ethical consideration important in research involving animals?
Ethical considerations are vital to ensure the welfare of animal subjects, prevent harm, and promote responsible research practices. This includes obtaining informed consent from human participants and ensuring the humane treatment of animals.
3. How can research on human-animal interactions impact public policy?
Research findings can inform policymakers about the benefits of positive human-animal relationships, leading to enhanced animal welfare regulations and community programs that promote responsible pet ownership and conservation efforts.

Statistical Methods
Statistical methods play a pivotal role in analyzing quantitative data derived from studies on human-animal interactions. By employing these techniques, researchers can uncover significant patterns and relationships that might otherwise go unnoticed. One of the most commonly used statistical methods is regression analysis, which helps to understand the relationship between a dependent variable—such as the emotional well-being of humans interacting with animals—and one or more independent variables, like the frequency of those interactions or the type of animal involved. This approach not only identifies correlations but also allows researchers to make predictions based on observed data.
Another important statistical tool is ANOVA (Analysis of Variance), which is particularly useful when comparing the means of three or more groups. For instance, if a study aims to evaluate the differences in stress levels among individuals interacting with therapy dogs, cats, and no animals at all, ANOVA can help determine whether the variations in stress levels are statistically significant. This is crucial for understanding which types of interactions yield the most beneficial outcomes for human participants.
To illustrate the application of these methods, consider the following
| Method | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Regression Analysis | To assess the impact of multiple variables on a single outcome | Studying how different types of animal interactions affect human anxiety levels |
| ANOVA | To compare means across multiple groups | Evaluating stress levels in people interacting with dogs, cats, and no animals |
These statistical methods not only enhance the credibility of research findings but also contribute to a deeper understanding of the nuances involved in human-animal relationships. By rigorously analyzing data, researchers can provide evidence-based recommendations that inform practices aimed at improving the welfare of both humans and animals. The insights gained through statistical analysis can ultimately lead to more effective policies and community programs designed to foster positive interactions between species.
- What is regression analysis?
Regression analysis is a statistical method used to determine the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables.
- Why is ANOVA important in research?
ANOVA is important because it helps researchers compare the means of three or more groups to see if there are any statistically significant differences.
- How can statistical methods improve human-animal interactions?
By providing data-driven insights, statistical methods can help identify best practices that enhance the benefits of human-animal interactions.

Thematic Analysis
Thematic analysis is a powerful qualitative research method that allows researchers to delve into the intricate world of human-animal interactions by identifying, analyzing, and reporting patterns (or themes) within qualitative data. This approach is particularly effective because it provides a rich and nuanced understanding of the emotional and social dimensions of these interactions. By examining participants' responses in detail, researchers can uncover the underlying meanings and experiences that shape human-animal relationships.
One of the key strengths of thematic analysis is its flexibility. It can be applied across various contexts and adapted to different research questions. For instance, when studying therapy animals, researchers might focus on themes such as comfort, trust, and emotional support. These themes can reveal how individuals perceive the role of animals in their lives, highlighting the profound impact that these relationships can have on mental health and well-being.
To conduct thematic analysis effectively, researchers typically follow a structured process that includes several stages:
- Familiarization: Researchers immerse themselves in the data, reading through transcripts and notes to gain a comprehensive understanding of the content.
- Initial Coding: This involves generating initial codes from the data, which are essentially labels that capture important features relevant to the research questions.
- Theme Development: Researchers then group these codes into broader themes that represent significant patterns within the data.
- Reviewing Themes: This stage involves refining and validating the themes to ensure they accurately reflect the data and research objectives.
- Defining and Naming Themes: Finally, researchers define what each theme represents and give them clear, descriptive names.
This method is not just about identifying themes; it’s about interpreting them in a way that provides insights into the complex dynamics of human-animal interactions. For example, a researcher might discover that themes related to companionship and emotional support are prevalent among pet owners, indicating the significant role pets play in enhancing human quality of life.
Moreover, thematic analysis can also highlight differences in experiences across various demographics, such as age, gender, or cultural background. This aspect is particularly valuable for understanding how different groups perceive and interact with animals, which can inform more tailored approaches to animal welfare and community programs.
In summary, thematic analysis serves as a crucial tool for researchers seeking to understand the multifaceted nature of human-animal relationships. Its ability to uncover deep insights and foster a greater understanding of these interactions makes it an invaluable component of research in this field.
- What is thematic analysis?
Thematic analysis is a qualitative research method that identifies and analyzes patterns or themes within qualitative data, providing insights into participants' experiences and perceptions.
- Why is thematic analysis important in studying human-animal interactions?
This method allows researchers to explore the emotional and social dimensions of human-animal relationships, revealing how these interactions impact well-being and behavior.
- How is thematic analysis conducted?
Thematic analysis involves familiarizing oneself with the data, coding it, developing themes, and interpreting those themes to draw meaningful conclusions.
- Can thematic analysis be used in quantitative research?
While thematic analysis is primarily a qualitative method, its findings can complement quantitative research by providing deeper context for statistical data.

Potential Impacts of Research
The research conducted on human-animal interactions holds immense potential to reshape our understanding and treatment of both humans and animals. By delving into the complexities of these relationships, researchers can uncover insights that lead to significant advancements in various fields. For instance, the findings can influence animal welfare policies, ensuring that animals receive better care and protection in different environments. Imagine a world where animals are not just seen as companions or tools, but as beings deserving of rights and respect. This shift in perspective can be catalyzed by robust research outcomes.
Moreover, research can help inform public policy, guiding legislators to create laws that enhance the quality of life for both animals and humans. For example, studies that demonstrate the therapeutic benefits of animal companionship can lead to increased funding for therapy animal programs in hospitals and schools. By translating research findings into actionable recommendations, communities can develop initiatives that foster positive interactions between species, ultimately benefiting everyone involved.
One of the most exciting aspects of this research is its potential to inspire community programs that promote healthy human-animal relationships. These programs can take many forms, such as:
- Therapy animal initiatives that provide emotional support to individuals in need
- Educational outreach programs that teach responsible pet ownership and animal care
- Conservation efforts aimed at protecting endangered species and their habitats
Each of these initiatives not only enhances the lives of animals but also enriches human communities by fostering empathy and understanding. For example, when children participate in educational programs about wildlife conservation, they develop a sense of responsibility towards the environment and the creatures that inhabit it. This kind of engagement is crucial for building a future where humans and animals coexist harmoniously.
In summary, the impacts of research on human-animal interactions are far-reaching. They extend beyond academia and into the realms of policy-making and community engagement. By prioritizing these studies, we can pave the way for a society that values the well-being of all its members, both human and animal alike. The ripple effects of this research can lead to a more compassionate world, where understanding and respect bridge the gap between species.
- What is the significance of studying human-animal interactions?
Understanding these interactions can improve animal welfare, inform public policy, and enhance community programs. - How can research findings be applied in real-life situations?
Findings can guide the development of therapy programs, educational initiatives, and conservation efforts. - What ethical considerations are involved in this type of research?
Research must prioritize animal welfare and obtain informed consent from human participants.

Policy Development
Research on human-animal interactions plays a crucial role in shaping effective . By understanding the intricate dynamics between humans and animals, policymakers can create informed guidelines that promote animal welfare and enhance the quality of life for both species. For instance, studies revealing the benefits of therapy animals in mental health settings can lead to policies that encourage the integration of these animals into healthcare programs.
Moreover, findings from research can inform regulations that protect animals in various environments. For example, if research highlights the negative impacts of certain practices on animal well-being, such as confinement in pet stores or inadequate shelter conditions, policymakers can implement stricter laws to ensure better treatment. This not only benefits the animals but also fosters a more compassionate society.
To illustrate the potential impacts of research on policy, consider the following areas:
| Research Findings | Potential Policy Implications |
|---|---|
| Benefits of therapy animals for mental health | Increased funding for therapy animal programs in hospitals and schools |
| Negative effects of urbanization on wildlife | Development of wildlife corridors and urban planning regulations |
| Public interest in sustainable pet ownership | Incentives for adopting from shelters instead of purchasing |
Additionally, community engagement is vital in the policy development process. By involving the public in discussions about animal welfare, policymakers can better understand community values and concerns. This participatory approach not only fosters trust but also ensures that policies reflect the needs and desires of the community. For example, local forums or surveys can be utilized to gather public input on proposed regulations affecting animal care and rights.
In conclusion, the implications of research on human-animal interactions extend far beyond academic circles. They hold the potential to transform policies that govern animal welfare, public health, and community well-being. As researchers continue to uncover valuable insights, it is imperative that these findings are translated into actionable policies that benefit both humans and animals alike.
- What is the importance of research on human-animal interactions? Research helps to understand the benefits and challenges of these relationships, informing policies that promote welfare and enhance quality of life.
- How can research findings influence public policy? Insights from studies can lead to the development of regulations that protect animals and improve human experiences with them.
- What role does community engagement play in policy development? Engaging the community ensures that policies reflect public values and concerns, fostering trust and cooperation.

Community Programs
Community programs play a pivotal role in enhancing the bond between humans and animals, creating an environment where both can thrive. These initiatives are not just beneficial; they are essential for fostering understanding and compassion towards our animal companions. Imagine a world where therapy animals visit schools, helping children with emotional challenges, or where community gardens welcome pets, promoting a sense of belonging among neighbors. Such interactions can transform lives, making community programs a vital part of social fabric.
One of the most impactful types of community programs is the therapy animal initiative. These programs often involve trained animals that provide comfort and support to individuals in hospitals, nursing homes, and schools. The presence of these animals can significantly reduce stress and anxiety, offering emotional relief to those in need. For example, therapy dogs can help children with autism develop social skills, while also providing companionship to the elderly, reminding them of the joy animals can bring.
In addition to therapy initiatives, educational outreach programs are crucial in teaching people about responsible pet ownership and animal welfare. These programs can include workshops, school visits, and community events that focus on topics such as:
- Understanding animal behavior
- Promoting spaying and neutering
- Encouraging adoption from shelters
By educating the public, we can cultivate a more compassionate society that values the welfare of all creatures. Moreover, these programs can lead to increased volunteerism, as community members become inspired to contribute their time and resources to local shelters and rescue organizations.
Another vital area is conservation efforts. Community programs that focus on wildlife conservation not only educate people about local ecosystems but also engage them in hands-on activities, such as habitat restoration and species monitoring. These initiatives create a sense of stewardship, encouraging participants to protect the environment and the animals that inhabit it. For instance, organizing clean-up days at local parks or nature reserves can have a profound impact, both on the environment and on participants' understanding of their role in preserving wildlife.
Ultimately, the success of community programs hinges on collaboration. Local governments, non-profit organizations, and citizens must work together to create and sustain these initiatives. By pooling resources and expertise, communities can develop programs that are not only effective but also sustainable in the long run. As we look towards the future, the potential for positive change through community programs is limitless, paving the way for a more harmonious relationship between humans and animals.
Q1: What are community programs focused on human-animal interactions?
A1: Community programs aimed at human-animal interactions include therapy animal initiatives, educational outreach, and wildlife conservation efforts. These programs foster positive relationships and understanding between humans and animals.
Q2: How can I get involved in community programs?
A2: You can get involved by volunteering at local shelters, participating in educational workshops, or joining conservation efforts in your area. Many organizations welcome community participation and support.
Q3: What benefits do therapy animals provide?
A3: Therapy animals offer emotional support, reduce stress and anxiety, and help individuals develop social skills. They are particularly beneficial in settings like schools and healthcare facilities.
Q4: How do community programs impact animal welfare?
A4: Community programs raise awareness about responsible pet ownership, promote adoption, and encourage humane treatment of animals, ultimately leading to improved animal welfare in the community.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is human-animal interaction?
Human-animal interaction refers to the various ways in which humans and animals engage with each other. This can include companionship, therapy, and even conservation efforts. These interactions have significant psychological, social, and economic implications, impacting both humans and animals in numerous ways.
- What research methodologies are used to study human-animal interactions?
Researchers often utilize a mix of qualitative and quantitative methods. Qualitative approaches might include interviews and focus groups to gather personal experiences, while quantitative methods could involve surveys and experiments to analyze data statistically. The choice of methodology depends on the specific research questions being addressed.
- Why are ethical considerations important in this type of research?
Ethical considerations are crucial because they ensure the welfare of both human and animal participants. This includes obtaining informed consent from human participants and ensuring the physical and psychological well-being of animal subjects. Adhering to ethical guidelines fosters trust and transparency in the research process.
- How is data analyzed in human-animal interaction research?
Data analysis techniques vary based on the type of data collected. For quantitative data, statistical methods like regression analysis and ANOVA are commonly used to identify patterns and relationships. For qualitative data, thematic analysis helps researchers identify recurring themes and insights from participant responses.
- What are the potential impacts of research on human-animal interactions?
This research can significantly influence animal welfare, public policy, and community programs. The findings can inform policies that promote better practices for animal care and enhance human experiences with animals, ultimately leading to improved relationships between the two.
- Can research findings lead to community programs?
Absolutely! Insights gained from studies on human-animal interactions can guide the development of community programs. These might include therapy animal initiatives, educational outreach, and conservation efforts, all of which aim to foster positive interactions and benefit both humans and animals.